Solar energy has emerged as a promising solution to our growing energy needs, offering a clean and sustainable alternative to conventional sources. Among the various solar technologies, solar domes stand out as innovative structures that efficiently capture and utilize sunlight. In this article, we will know all about the solar domes, exploring their design, benefits, and the role they play in advancing renewable energy.
What are Solar Domes?
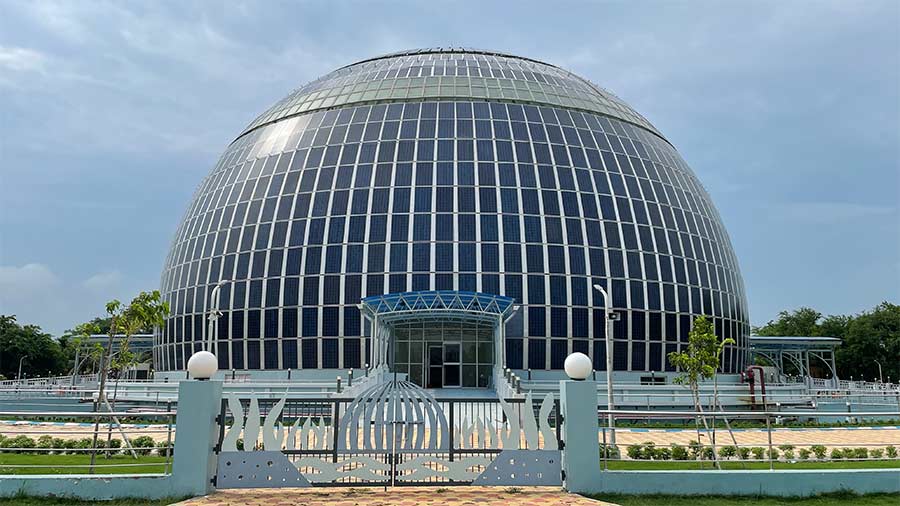
Solar domes are architectural marvels designed to capture and harness sunlight for energy production. Resembling giant, transparent bubbles, these structures use advanced materials to allow sunlight to pass through while trapping the solar energy inside. This trapped energy is then converted into electricity, providing a renewable and eco-friendly power source.

Design and Structure:
Solar domes come in various shapes and sizes, but the basic principle remains the same – maximizing sunlight exposure. The structure typically consists of a transparent outer layer made from materials like glass or specialized plastics, which allows sunlight to penetrate while preventing heat loss. Beneath this outer layer is the energy conversion system, which can include photovoltaic cells, solar thermal collectors, or a combination of both.
Photovoltaic cells convert sunlight directly into electricity, while solar thermal collectors use sunlight to generate heat that can be used to produce electricity through traditional turbines or stored for later use. The careful integration of these components ensures that solar domes are efficient in capturing and utilizing sunlight throughout the day.
Advantages of Solar Domes:
Solar domes offer several advantages that contribute to their growing popularity in the renewable energy landscape:
a. Space Efficiency: Solar domes can be built in various environments, including urban areas with limited space. Their compact design allows for the efficient use of available land, making them suitable for both residential and commercial applications.
b. Weather Resistance: The transparent outer layer of solar domes is often designed to withstand harsh weather conditions, including hail and strong winds. This durability ensures a consistent and reliable energy output, even in challenging climates.
c. Increased Energy Yield: The design of solar domes enables them to capture sunlight from multiple angles, maximizing energy yield throughout the day. This is particularly advantageous in regions with variable weather patterns or limited sunlight hours.
d. Aesthetically Pleasing: Solar domes can be aesthetically pleasing additions to the landscape, blending functionality with architectural appeal. This makes them a viable option for integrating renewable energy solutions into urban and suburban environments.
e. Modular Construction: The modular nature of solar domes allows for scalability and ease of installation. Multiple units can be interconnected to create larger energy-generating facilities, adapting to the specific energy needs of a given location.
Applications of Solar Domes:
Solar domes find applications across various sectors, showcasing their versatility in meeting diverse energy requirements:
a. Residential Use: Small-scale solar domes can be employed in residential areas to supplement household energy needs. These structures can be integrated into rooftops or standalone installations in backyards, providing homeowners with a reliable source of clean energy.
b. Commercial and Industrial Facilities: Larger solar dome installations are well-suited for commercial and industrial facilities with higher energy demands. These structures can power manufacturing processes, warehouses, and office spaces, contributing to significant cost savings over time.
c. Agricultural Sector: Solar domes can be utilized in agriculture for controlled environment farming. By providing a consistent and controlled climate, these structures enhance crop yields and allow for year-round cultivation, independent of external weather conditions.
d. Energy Parks: Solar domes can be combined to create energy parks, generating substantial electricity for local communities. These parks serve as decentralized power sources, reducing the reliance on centralized energy grids and promoting energy independence.
e. Disaster Relief: In emergency situations, solar domes can serve as temporary power solutions, providing electricity for essential services such as lighting, communication, and medical equipment. Their quick and modular installation makes them valuable assets in disaster-stricken areas.
Future Trends and Innovations:
As technology advances, the field of solar domes continues to evolve with several exciting trends and innovations:
a. Smart Integration: Solar domes are increasingly being equipped with smart technologies that enhance their efficiency. Automated tracking systems, sensors, and machine learning algorithms allow these structures to optimize sunlight capture and energy production based on real-time environmental conditions.
b. Advanced Materials: Ongoing research focuses on developing advanced materials for the outer layer of solar domes. Innovations in materials science aim to enhance transparency, durability, and resistance to environmental factors, further improving the overall performance of these structures.
c. Energy Storage Solutions: Integrating efficient energy storage solutions with solar domes addresses the intermittent nature of solar power. Batteries and other storage technologies enable the storing of excess energy during peak sunlight hours for use during periods of low sunlight or at night.
d. Hybrid Systems: Hybrid solar dome systems, combining photovoltaic cells with other renewable technologies such as wind or geothermal, are emerging as comprehensive solutions for sustainable energy generation. These hybrid systems can provide a consistent power supply by harnessing multiple renewable sources.
Conclusion
Solar domes represent a significant stride towards a more sustainable and cleaner energy future. Their innovative design, coupled with numerous advantages and diverse applications, positions them as key players in the global shift towards renewable energy. As research and development continue to drive advancements in solar technology, we can expect solar domes to play an increasingly vital role in meeting our energy needs while minimizing environmental impact.
Projects around the World on Solar Domes
- Bengal’s Silicon Valley, Eco Park, New Town, Kolkata: This project has been jointly executed by HIDCO (West Bengal Housing Infrastructure Development Corporation Ltd) and WBSEDCL (West Bengal State Electricity Distribution Company). The solar dome has 2000 active solar panels which continuously generate solar power.
- NEOM, Saudi Arabia: Saudi Arabia is planning to build the world’s first “solar dome” desalination plants at Neom, a mega-city that it’s developing along the country’s northern Red Sea coast. The solar dome plants will produce no carbon emissions and create less brine than facilities using conventional reverse osmosis technology.
You May Also Like

What a fantastic idea!
I wonder how the photovoltaic panels can not get too hot in there (which reduces their efficiency), because it is a kind of greenhouse.
Perhaps at least the ambient heat is removed and used…
Vincent, France
LikeLiked by 1 person