In a world increasingly concerned about environmental issues, green hydrogen has emerged as a promising solution. But what exactly is green hydrogen, and what is it used for? In this guide, we’ll explore the what is green hydrogen, its production, and the numerous applications that make it a key player in the shift towards a more sustainable future.
Understanding Green Hydrogen
To comprehend what green hydrogen is used for, we must first grasp what green hydrogen is and how it’s produced.
What is Green Hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is hydrogen gas (H2) produced through a process known as electrolysis, using renewable energy sources like wind or solar power. Unlike grey or blue hydrogen, which is derived from fossil fuels and emits harmful greenhouse gases, green hydrogen is produced without carbon emissions.
How is Green Hydrogen Produced?
The production of green hydrogen involves splitting water into its two basic components, hydrogen and oxygen, using electricity. The key steps are as follows:
- Electrolysis: Electricity is applied to water, causing it to separate into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Collection and Storage: The hydrogen is collected, purified, and stored for future use.
Applications of Green Hydrogen
Now that we have a solid understanding of green hydrogen, let’s look into the many applications that are driving its adoption.
Fueling Transportation
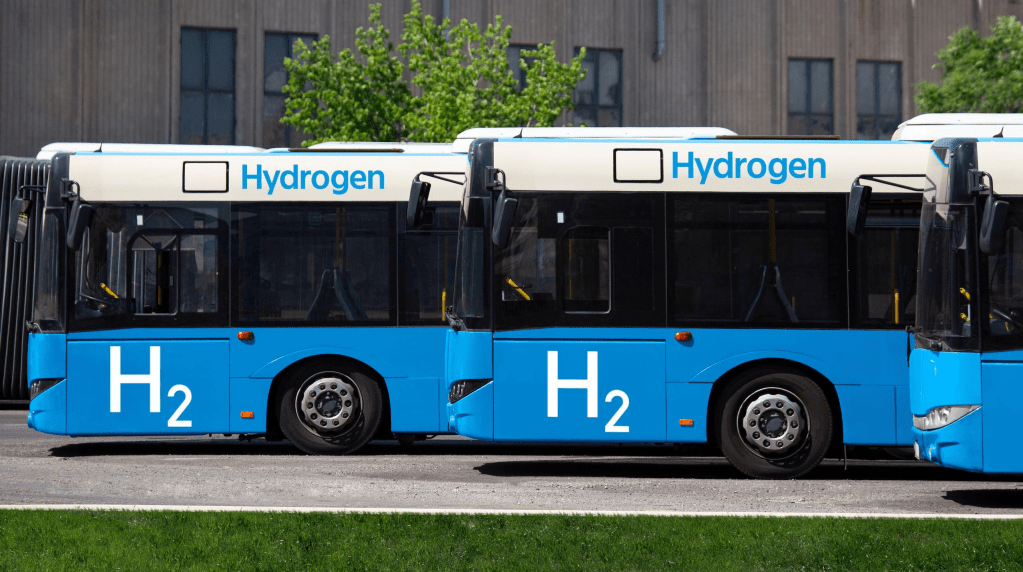
One of the most exciting uses of green hydrogen is in the transportation sector. Hydrogen fuel cells can power a variety of vehicles, including cars, trucks, buses, and trains. These cells convert hydrogen into electricity to drive an electric motor, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct.
Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are at the forefront of this revolution, offering a promising solution for sustainable transportation. These vehicles are equipped with a hydrogen tank that connects to a fuel cell, where the magic happens. Inside the fuel cell, hydrogen and oxygen react, generating electricity that powers the vehicle’s engine. The only byproduct of this reaction is water vapor, making FCEVs a genuinely eco-friendly option. While FCEVs currently represent only a small fraction (0.5%) of new low-emission vehicle sales, the International Energy Agency predicts that the market for FCEVs is on the verge of a significant expansion. Several key players in the automotive industry are already making substantial investments in this technology.
Cities around the world are also taking steps to integrate green hydrogen into their public transportation systems. For instance, Paris is in the process of developing a fleet of hydrogen-powered taxis, contributing to reduced emissions and improved air quality in the city.
In several European cities, waste collection vehicles have already embraced green hydrogen technology. These vehicles are being powered by hydrogen fuel cells, reducing emissions associated with waste management while setting an example for the potential applications of green hydrogen in various sectors.
Decarbonizing Industry
Green hydrogen plays a significant role in decarbonizing industrial processes. It can be used as a clean and efficient energy source for various applications, including:
- Steel and Chemical Production: Green hydrogen can replace carbon-intensive processes in these industries, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Refineries: It can be used to reduce emissions from hydrogen production in refineries.
- Ammonia Production: Green hydrogen is a crucial component in ammonia production, which is essential for fertilizers and other industrial processes.
Energy Storage
Green hydrogen can be stored and used as an energy carrier. During periods of excess renewable energy generation, such as sunny or windy days, surplus electricity can be used to produce green hydrogen, which can then be stored and later used to generate electricity when needed, thus acting as a backup power source.
Power Generation
Green hydrogen can be used in power generation, particularly when grid-scale electricity storage is required. Hydrogen can be burned in turbines to produce electricity or used in fuel cells to generate power efficiently and with minimal emissions.
Also Read: Renewable Energy: What are New Emerging Trends?
What are the advantages of green hydrogen technologies compared with other renewables?
Let us also explore the numerous advantages of green hydrogen, making it a crucial element in the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
Environmental Benefits
Green hydrogen is a clean and sustainable energy carrier, emitting no carbon dioxide during its production or use. This makes it an essential tool in the fight against climate change and air pollution.
Energy Security
Hydrogen can be produced domestically using renewable energy sources, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and enhancing energy security.
Versatility
Green hydrogen is incredibly versatile, with applications in transportation, industry, energy storage, and power generation, making it a flexible energy solution.
Economic Opportunities
The growing green hydrogen industry creates jobs and economic opportunities, helping regions transition from fossil fuel-based economies to cleaner, more sustainable ones.
Also Read: Exploring the Advantages of Green Hydrogen for a Sustainable Future
Challenges and Limitations
While green hydrogen shows tremendous promise, it’s important to understand the challenges and limitations it faces.
High Production Costs
Currently, the production of green hydrogen can be more expensive than fossil fuel-based hydrogen due to the cost of renewable energy sources and electrolysis equipment.
Energy Conversion Efficiency
The process of converting electricity to hydrogen and then back to electricity in fuel cells can result in energy losses, reducing overall efficiency.
Infrastructure Development
The widespread adoption of green hydrogen requires significant infrastructure development, including the construction of hydrogen production facilities, distribution networks, and refueling stations.
In conclusion, green hydrogen is a clean, versatile, and sustainable energy carrier that is poised to play a significant role in addressing environmental challenges and advancing energy transition efforts. As technology improves and adoption increases, the potential for green hydrogen to reshape the energy landscape and reduce carbon emissions is brighter than ever.
You May also Like

