Electric cars have gained popularity in recent years, offering an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. One of the essential aspects of owning an electric car is knowing how to charge it. In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about charging your electric car.
Types of Electric Car Chargers
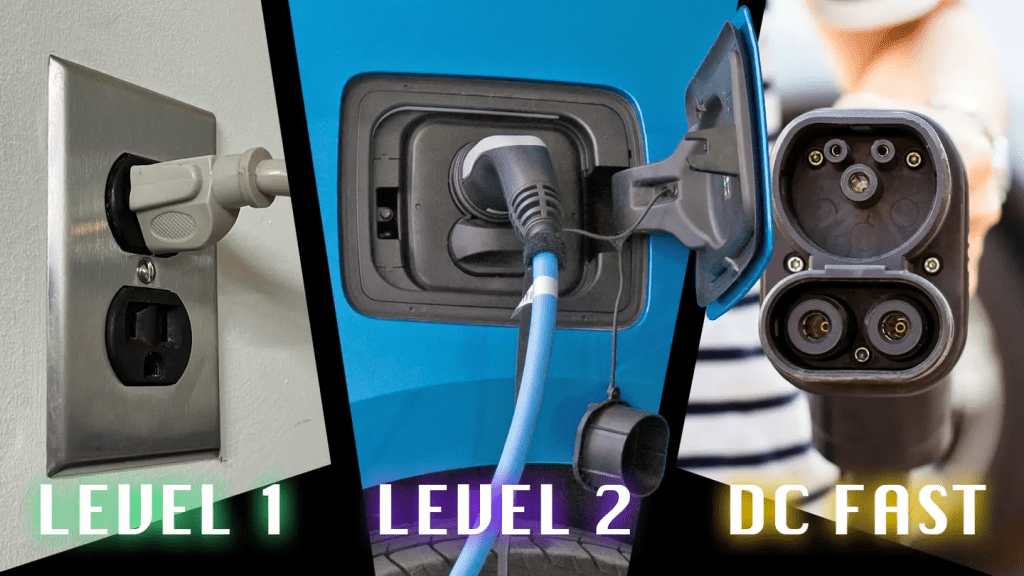
There are three main types of electric car chargers:
a. Level 1 Charger: This charger uses a standard 120-volt household outlet. It’s the slowest option but can be convenient for overnight charging at home.
b. Level 2 Charger: These chargers use a 240-volt outlet, similar to what you’d use for a dryer or stove. They charge your car faster than Level 1 chargers and are ideal for home charging or public charging stations.
c. DC Fast Charger: These chargers provide a rapid charge and are typically found at public charging stations. They can charge your car’s battery to 80% capacity in around 30 minutes.
Also Read: Top 8 Reasons to Buy an Electric Car
How and Where to Charge an Electric Car
harging your electric car is simple, and you can do it in various places:
- At Home: The most convenient and common place to charge your electric car is at home. You’ll need a Level 1 or Level 2 charging station, which can be installed by an electrician. Plug your car into the charger, and it will charge while you’re at home, usually overnight.
- Public Charging Stations: You can charge your electric car at public charging stations, which are located in various places like shopping centers, parking lots, and along highways. Use smartphone apps or GPS to find these stations. Some are free, while others require payment or a membership.
- Workplace Charging: Some workplaces provide charging stations for their employees. If your workplace offers this perk, you can charge your car while you work.
- Destination Charging: Certain hotels, restaurants, and tourist attractions have electric vehicle charging stations available for visitors. This can be convenient for topping up your battery while you enjoy your destination.
- DC Fast Chargers: These high-speed chargers are typically found at highway rest areas and service stations. They provide rapid charging, allowing you to get back on the road quickly.
Home Charging

Charging your electric car at home is convenient and cost-effective. To set up home charging, you’ll need:
- An electrician to install a Level 2 charging station.
- Access to a 240-volt outlet or a dedicated circuit.
- A charging cable that comes with your car.
Simply plug in your car at night, and it’ll be ready to go in the morning.
Also Read: Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Electric Cars
Public Charging

When you’re on the road, you can charge your electric car at public charging stations. Here’s what you need to know:
- Locate charging stations using smartphone apps or GPS.
- Different networks might require membership or offer pay-as-you-go options.
- Follow instructions at the station to plug in your car and pay for the charge.
Charging Time
Charging time varies depending on several factors:
- Charger Type: Level 1 chargers are the slowest, taking many hours for a full charge. Level 2 chargers are faster, usually requiring a few hours. DC Fast Chargers are the quickest, providing an 80% charge in about 30 minutes.
- Battery Capacity: The size of your car’s battery plays a role. A larger battery will take longer to charge fully.
- Starting Battery State: If your battery is nearly empty, it will take longer to charge than if it’s partially full.
In general, most electric cars can be charged overnight at home with a Level 2 charger, making it ready for your daily commute.
Charging Costs
The cost of charging your electric car depends on:
- Electricity Rates: The cost of electricity in your area. Charging at home is typically cheaper than using public charging stations.
- Charging Station Fees: Some public charging stations have a fee for use, which can vary widely. Some stations offer free charging.
- Charger Type: DC Fast Chargers are often more expensive per kWh than Level 2 chargers.
- Your Car’s Efficiency: Different electric cars have varying levels of energy efficiency, so the cost to charge may differ from one model to another.
You can calculate the cost of charging by multiplying the number of kilowatt-hours (kWh) used by the cost per kWh. This information can usually be found on your electricity bill or at the charging station.
Charging Safety
Charging your electric car is safe, but it’s essential to follow safety guidelines:
- Ensure your charging equipment is in good condition.
- Don’t use damaged cables.
- Be cautious during storms and avoid charging in flooded areas.
Charging your electric car is a straightforward process, whether you do it at home or at a public station. Understanding the types of chargers, where to find them, and how long it takes can make your electric car ownership experience smooth and hassle-free. This is the future of transportation that will help reduce your carbon footprint by driving an electric car!
FAQs about Charging an Electric car
- How do I charge my electric car at home?
- To charge your electric car at home, you’ll need a Level 1 or Level 2 charging station, a 240-volt outlet, and a charging cable that came with your car. Simply plug in your car, and it will charge overnight.
- Can I charge my electric car with a regular household outlet?
- Yes, you can use a regular 120-volt household outlet (Level 1 charger) to charge your electric car, but it will be slower than using a Level 2 charger.
- How long does it take to charge an electric car at a public charging station?
- The charging time at a public station depends on the charger type and your car’s battery capacity. Level 2 chargers are faster and take a few hours, while DC Fast Chargers can provide an 80% charge in around 30 minutes.
- How much does it cost to charge an electric car?
- Charging costs vary depending on your location and the charging network. Some stations offer free charging, while others charge per kilowatt-hour (kWh) or by the minute. It’s generally cheaper than gasoline.
- Can I overcharge my electric car?
- No, modern electric cars have built-in safety features that prevent overcharging. Once the battery is fully charged, the charging process stops automatically.
- Is it safe to charge my electric car in the rain?
- Charging your electric car in light rain is generally safe. However, avoid charging during heavy storms or in flooded areas to minimize the risk of electrical hazards.
- Do I need a special adapter to charge my electric car at different charging stations?
- In most cases, you won’t need a special adapter. Electric cars come with a standard charging connector that fits into most public charging stations. However, it’s a good idea to carry an adapter just in case.
- Can I charge my electric car with a portable charger?
- Yes, you can use a portable charger (Level 1) to charge your electric car in emergencies or when away from home. It’s slower than Level 2 chargers but can be handy.
- How can I find nearby charging stations?
- You can use smartphone apps, GPS, or online maps to locate nearby charging stations. Many electric car manufacturers also provide apps that help you find compatible stations.
- Is it possible to overuse public charging stations?
- Public charging stations are designed for regular use, and you won’t damage them by frequent charging. However, be considerate of other electric car owners and avoid “icing” (blocking) charging spots when not charging.
You May Also Like