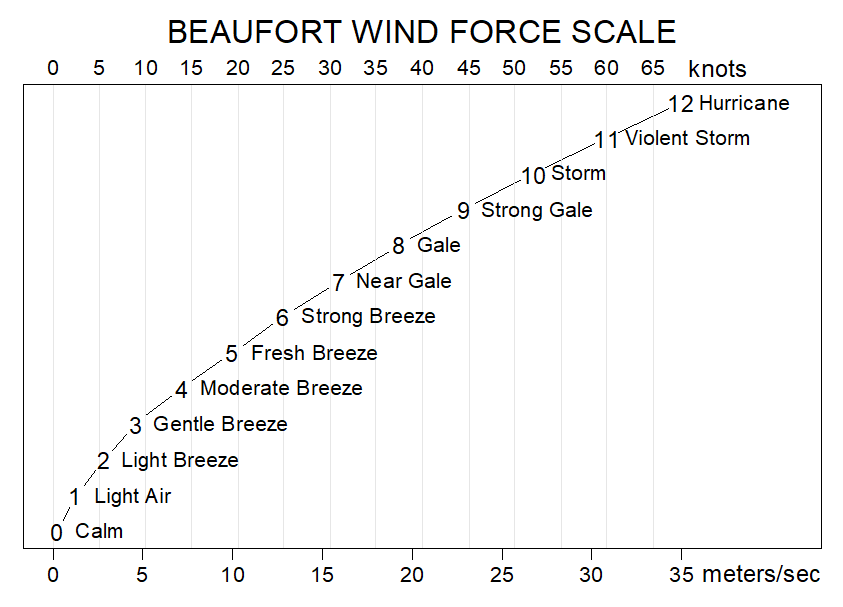
The Beaufort scale is a system used to estimate and describe wind speeds based on observable effects on land or sea. It was developed in the early 19th century by Sir Francis Beaufort, a British naval officer. The scale provides a standardized way to communicate and categorize wind strength, helping sailors, meteorologists, and others assess and compare wind conditions.
The Beaufort scale consists of 13 numerical values, ranging from 0 to 12, each corresponding to a specific range of wind speeds and their associated effects. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the Beaufort scale:
0: Calm – Smoke rises vertically; sea surface is smooth.
1: Light air – Wind direction is indicated by smoke drift, but not by wind vanes.
2: Light breeze – Wind can be felt on the face; leaves rustle; wind vanes move.
3: Gentle breeze – Leaves and small twigs are in constant motion; flags extend.
4: Moderate breeze – Dust and loose paper are raised; small branches move.
5: Fresh breeze – Small trees sway; waves on water begin to form.
6: Strong breeze – Large branches sway; umbrellas difficult to control.
7: High wind, near gale – Whole trees in motion; walking against the wind is difficult.
8: Gale – Twigs and small branches are broken off; progress is impeded.
9: Strong gale – Slight structural damage occurs; chimney pots and slates may fall.
10: Storm – Trees uprooted; considerable damage to buildings and vegetation.
11: Violent storm – Widespread damage; very high waves on the sea.
12: Hurricane – Devastation occurs; exceptionally high waves and airborne debris.
The Beaufort scale provides a standardized way to communicate wind conditions and their potential impact. It helps sailors determine appropriate sail configurations, aids meteorologists in reporting weather conditions, and enables individuals to understand and compare wind strength in different situations.
It’s important to note that the Beaufort scale is subjective and based on observations rather than precise measurements. Modern weather monitoring uses instruments like anemometers to provide accurate wind speed measurements, but the Beaufort scale remains a valuable tool for quick and practical wind assessment in various contexts.
MCQs
- Who developed the Beaufort scale?
- a) Sir Francis Drake
- b) Sir Francis Bacon
- c) Sir Francis Beaufort
- d) Sir Francis Scott Key
- What is the purpose of the Beaufort scale?
- a) To measure rainfall intensity
- b) To estimate wind speeds
- c) To assess earthquake magnitudes
- d) To determine ocean wave heights
- How many numerical values are there in the Beaufort scale?
- a) 5
- b) 10
- c) 12
- d) 15
- What does a Beaufort scale value of 0 indicate?
- a) Calm conditions
- b) Gentle breeze
- c) Gale-force winds
- d) Hurricane conditions
- At which Beaufort scale value does the wind reach hurricane strength?
- a) 8
- b) 10
- c) 11
- d) 12
- How Plastic Pollution Is Choking Our Oceans And 12 Real Ways You Can Fix It

- 2025 Outlook: Top Global Trends Shaping the Future of Tech, Lifestyle, Sustainability and Culture

- 10 Eco-Friendly Gift Ideas for People Who Care About the Planet

- Audiobooks vs E-books: Which Is More Eco-Friendly?

- Why Audiobooks Are the Most Sustainable Way to Learn

