Last Updated: January 2026
INTRODUCTION
Symbiosis is a biological interaction in which two different organisms live in close association for a prolonged period, influencing survival, nutrition, and reproduction. These interactions play a crucial role in shaping ecosystems, influencing survival, reproduction, and population dynamics.
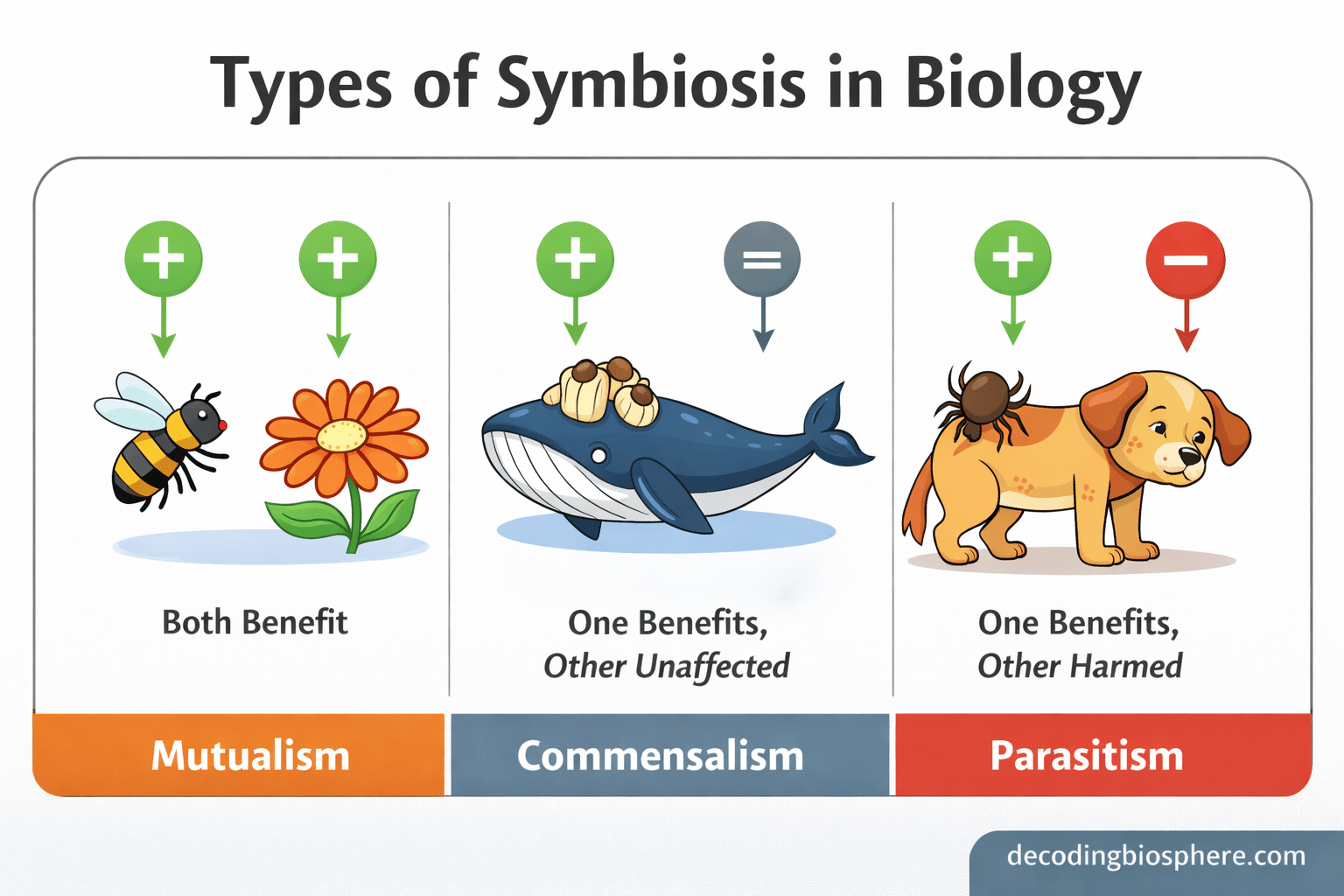
In biology, symbiotic relationships are broadly classified based on how each organism is affected. Understanding the types of symbiosis helps explain ecological balance, species interdependence, and biodiversity patterns in nature.
AT-A-GLANCE TABLE
| Type of Symbiosis | Effect on Species A | Effect on Species B | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mutualism | Benefits | Benefits | Bees and flowers |
| Commensalism | Benefits | No effect | Barnacles on whales |
| Parasitism | Benefits | Harmed | Tapeworm in humans |
| Amensalism | Harmed | No effect | Penicillium inhibiting bacteria |
1️⃣ MUTUALISM
Definition:
Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship in which both organisms benefit from the interaction.
Examples:
- Bees and flowering plants: Bees obtain nectar, while plants are pollinated.
- Lichens: Algae produce food; fungi provide shelter and moisture.
Ecological importance:
- Enhances reproduction
- Improves nutrient cycling
- Strengthens ecosystem stability
👉 This interaction is explained in detail under biological associations.
2️⃣ COMMENSALISM
Definition:
Commensalism occurs when one organism benefits while the other is neither harmed nor benefited.
Examples:
- Barnacles on whales: Barnacles gain mobility and food access.
- Epiphytic orchids on trees: Orchids gain sunlight without harming trees.
Key point:
The host remains unaffected.
3️⃣ PARASITISM
Definition:
Parasitism is a symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits at the expense of the other.
Examples:
- Tapeworms in humans
- Ticks on mammals
- Mistletoe on trees
Impact:
- Weakens host
- Can cause disease or death
- Influences population control
4️⃣ AMENSALISM
Definition:
Amensalism is a relationship where one organism is harmed, while the other remains unaffected.
Examples:
- Penicillium fungus producing antibiotics that inhibit bacteria
- Large animals trampling vegetation
SYMBIOSIS vs OTHER BIOLOGICAL INTERACTIONS
Symbiosis is a subset of biological associations, which also include predation and competition. Unlike short-term interactions, symbiosis usually involves long-term coexistence between species.
👉 Read more about interaction types in Biological Association: Types and Examples
Examples of Symbiosis in Real Ecosystems”
- Coral reefs (coral + zooxanthellae)
- Forests (mycorrhizae)
- Grasslands (grazers + microbes)
Explore Related Biology Concepts
- Mutualism in Biology
- Commensalism and Parasitism
- Biological Association: Types and Examples
- Species Adaptations in Xeric and Mesic Habitats
FAQ SECTION
❓ What is symbiosis in biology?
Symbiosis is a long-term biological interaction between two different species living closely together.
❓ What are the main types of symbiosis?
The main types are mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, and amensalism.
❓ Is parasitism a form of symbiosis?
Yes, parasitism is considered a symbiotic relationship because organisms live in close association.
❓ Why is symbiosis important?
Symbiosis helps maintain ecosystem balance, nutrient flow, and species survival.
MCQs on Symbiosis in Biology
1. Symbiosis is best defined as:
a) A short-term interaction between organisms
b) A relationship where one organism always harms another
c) A long-term association between two different species
d) Interaction occurring only in parasites
Answer: c) A long-term association between two different species
2. Which of the following is an example of mutualism?
a) Tapeworm in human intestine
b) Barnacles on whales
c) Bees and flowering plants
d) Lion and zebra
Answer: c) Bees and flowering plants
3. In commensalism, the relationship between organisms is such that:
a) Both organisms benefit
b) One benefits and the other is harmed
c) One benefits and the other is unaffected
d) Both organisms are harmed
Answer: c) One benefits and the other is unaffected
4. Barnacles attached to whales represent which type of symbiosis?
a) Mutualism
b) Parasitism
c) Amensalism
d) Commensalism
Answer: d) Commensalism
5. Which of the following correctly represents parasitism?
a) Lichen (algae + fungi)
b) Epiphytic orchids on trees
c) Tapeworm living in humans
d) Bees pollinating flowers
Answer: c) Tapeworm living in humans
6. In parasitism, the parasite:
a) Benefits the host
b) Is unaffected by the host
c) Benefits at the expense of the host
d) Kills the host immediately
Answer: c) Benefits at the expense of the host
7. Amensalism is a relationship in which:
a) Both organisms benefit
b) One organism is harmed and the other is unaffected
c) One organism benefits and the other is harmed
d) Both organisms are unaffected
Answer: b) One organism is harmed and the other is unaffected
8. Penicillium producing antibiotics that inhibit bacterial growth is an example of:
a) Mutualism
b) Commensalism
c) Parasitism
d) Amensalism
Answer: d) Amensalism
9. Which type of symbiosis plays a major role in pollination and nutrient cycling?
a) Parasitism
b) Amensalism
c) Mutualism
d) Competition
Answer: c) Mutualism
10. Symbiosis differs from predation because symbiosis:
a) Is always harmful
b) Is a short-term interaction
c) Involves long-term close association
d) Occurs only in animals
Answer: c) Involves long-term close association