📱 What Is E-Waste and Why Is It a Big Deal?
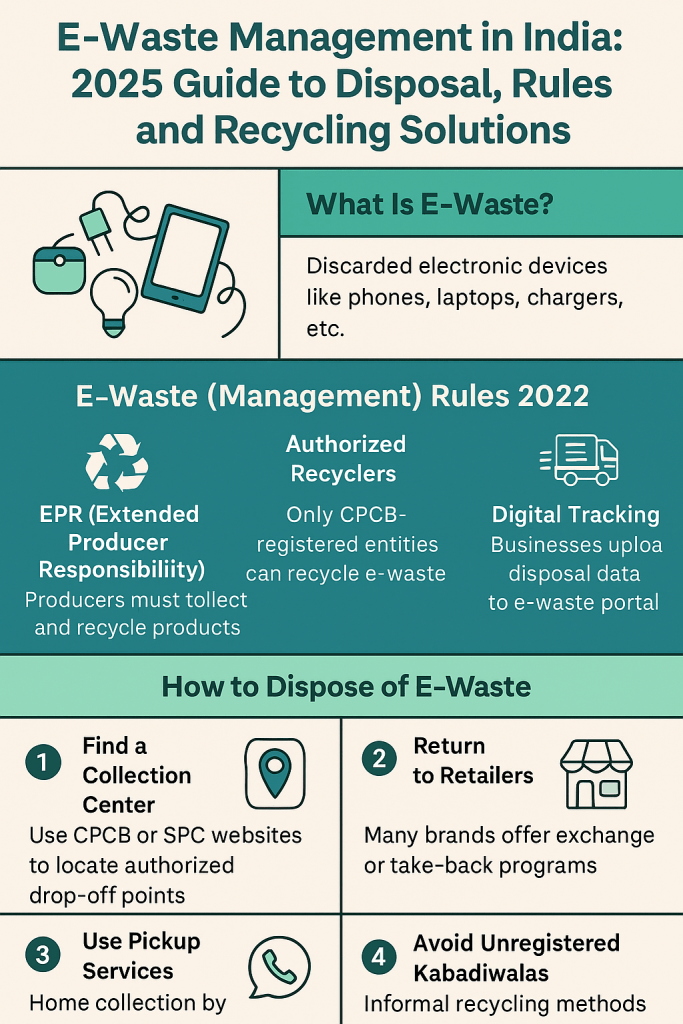
Electronic waste, or e-waste, refers to discarded electrical or electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, TVs, chargers, and batteries. In India, the explosion of digital usage and shorter product lifecycles has created a mounting e-waste crisis.
According to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), India generated 1.6 million tonnes of e-waste in 2023–24, and this number is projected to rise by 30% annually.
📊 Key Facts About E-Waste in India (2025 Update)
- India ranks 3rd globally in e-waste generation (after China and the US).
- Only 20% of e-waste is formally recycled; the rest goes to informal, unregulated handlers.
- 95% of e-waste workers are in the unorganized sector, often without safety or environmental safeguards.
- New E-Waste (Management) Rules 2022, effective from April 1, 2023, have tightened compliance for manufacturers and recyclers.
✅ Who Generates E-Waste?
| Source | Examples |
|---|---|
| Households | Phones, chargers, appliances |
| Offices & IT Sector | Laptops, servers, printers |
| Retail & E-commerce | POS systems, display units |
| Educational Institutions | Projectors, lab equipment |
| Healthcare Sector | Diagnostic devices, monitors |
🏛️ What Do the E-Waste Management Rules Say?
India’s latest E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022, aim to streamline and formalize recycling efforts. Key provisions include:
🔹 Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
- Manufacturers and importers are responsible for collecting and recycling end-of-life products.
- EPR certificates are now mandatory.
🔹 Authorized Recyclers
- Only CPCB-registered entities are allowed to recycle or refurbish e-waste.
- Informal recycling is considered illegal and hazardous.
🔹 Digital Portal for E-Waste Tracking
- Companies must upload collection, recycling, and disposal data to a central e-waste tracking portal managed by CPCB.
🔗 More info: CPCB E-Waste Portal
🛠️ How to Dispose of E-Waste Responsibly in 2025
1. 📦 Find a Nearby Authorized Collection Center
Use the CPCB or SPCB websites to locate government-registered e-waste drop-off points in your city.
2. 🔄 Exchange or Return to Retailers
Most major electronics brands (e.g., Samsung, Apple, HP, Dell) offer take-back or exchange programs under EPR.
3. ♻️ Use Certified E-Waste Recyclers
Look for recyclers registered with CPCB like:
- Attero Recycling
- Karo Sambhav
- Ecoreco
- Green Waves
4. 📞 Schedule E-Waste Pickups
Many recyclers and NGOs like SAAHAS Zero Waste, Namo E-Waste, and EcoReco offer home pickup services in urban areas.
5. 🧴 Avoid Giving to Kabadiwalas (Unless Certified)
Unorganized sector recycling may involve toxic dismantling, open burning, or chemical acid extraction—harmful to workers and the environment.
💡 What You Can Recycle
| ✅ Acceptable Items | 🚫 Avoid These |
|---|---|
| Phones, tablets, chargers | CFL bulbs, batteries (need separate disposal) |
| Laptops, PCs, printers | Wet waste or household junk |
| Cables, routers, keyboards | Plastic toys or non-electronic items |
🔄 Upcycle or Donate Before You Recycle
- Schools and NGOs often accept working devices.
- Turn old phones into security cameras or music players.
- Use dead motherboards creatively for wall art or DIY clocks.
🙋♀️ Frequently Asked Questions
❓ What happens if I don’t dispose of e-waste properly?
It may leach toxic substances (lead, mercury, cadmium) into soil and water and violate the 2022 rules.
❓ Are e-waste pickup services free?
Some NGOs offer free pickup; others may charge based on item type and distance.
❓ Can I recycle batteries and CFL bulbs here?
No. They require hazardous waste handling and must be sent to specialized facilities.
🧭 Next Steps: Your 2025 E-Waste Action Plan
✅ Declutter all unused electronics every 6 months
✅ Check product warranty or exchange eligibility
✅ Use only CPCB-approved recyclers
✅ Track your e-waste footprint with a disposal log
✅ Educate your community or RWAs
📢 Final Thoughts
India’s digital boom should not come at the cost of its environment. E-waste management is no longer just a corporate responsibility—it starts at home. By following the rules, choosing safe recyclers, and spreading awareness, you can be part of the circular tech future India needs.
💬 Do you have e-waste sitting at home? Share how you plan to dispose of it in the comments!
Pin this