Peninsulas, characterized by their protrusion of land surrounded by water on three sides, are prominent geographical features found across the world. They play a significant role in shaping coastlines, influencing maritime trade routes, and harboring diverse ecosystems. In this article, we will understand the formation of peninsulas, the geological processes that give rise to these landforms, and explore examples of the ten largest peninsulas on Earth.
Understanding the Formation of Peninsulas
Peninsulas are typically formed through a combination of geological processes, including erosion, deposition, tectonic activity, and sea level changes. The specific formation of a peninsula depends on factors such as the local geology, coastline morphology, and regional tectonic activity. Here’s an overview of the primary mechanisms involved in the formation of peninsulas:
1.Erosion and Deposition:
The action of wind, water, and ice plays a crucial role in shaping coastlines and carving out peninsulas over time. Coastal erosion, driven by waves, currents, and weathering processes, gradually wears away softer rock layers, creating headlands, cliffs, and bays. Sediment deposition, carried by rivers, tides, and ocean currents, can accumulate along coastal areas, extending the landmass and forming sandy beaches and coastal plains.
2. Tectonic Activity:
Tectonic forces, including crustal uplift, faulting, and folding, can influence the formation and evolution of peninsulas. Subduction zones, where one tectonic plate descends beneath another, can lead to the uplift of coastal mountain ranges and the emergence of peninsulas along convergent plate boundaries. Tectonic rifting, occurring along divergent plate boundaries, can also create rift valleys and elongated peninsulas as continents drift apart.
3. Sea Level Changes:
Fluctuations in sea level, driven by factors such as climate change, glaciation, and tectonic movements, can alter coastal landscapes and contribute to the formation of peninsulas. During periods of low sea level, exposed continental shelves and coastal plains may emerge, connecting previously isolated landmasses and creating expansive peninsulas. Conversely, rising sea levels can submerge low-lying coastal areas, transforming peninsulas into islands or narrowing their land connections.
Examples of the Ten Largest Peninsulas in the World
1. Arabian Peninsula
Location: Southwest Asia
Countries: Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait
Features: Desert landscapes, rugged mountains, coastal plains, and the Rub’ al Khali (Empty Quarter) desert.

2. Indochinese Peninsula
Location: Southeast Asia
Countries: Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand, Myanmar (Burma), Malaysia
Features: Tropical rainforests, Mekong River delta, Annamite Mountains, and diverse cultural heritage.
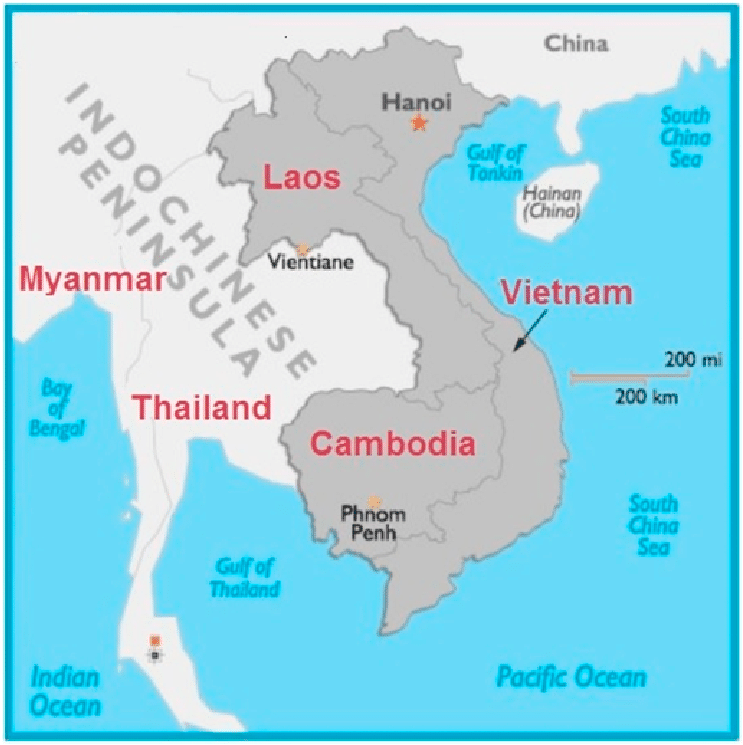
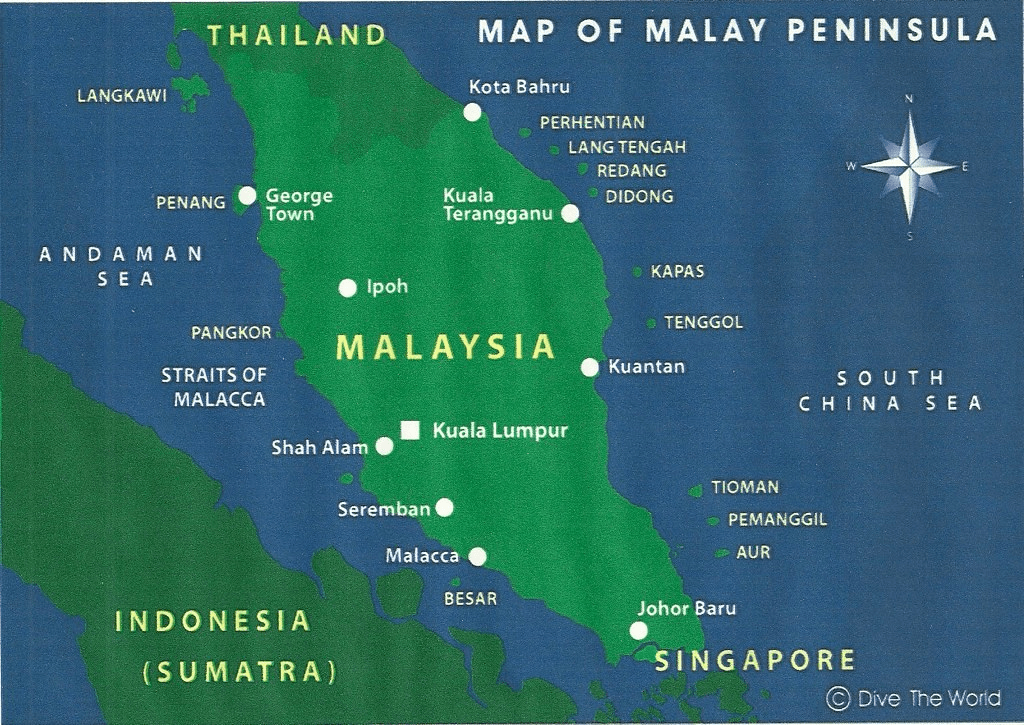
3. Malay Peninsula
Location: Southeast Asia
Countries: Malaysia, Singapore
Features: Dense rain-forests, coastal mangroves, Cameron Highlands, and the bustling city-state of Singapore.
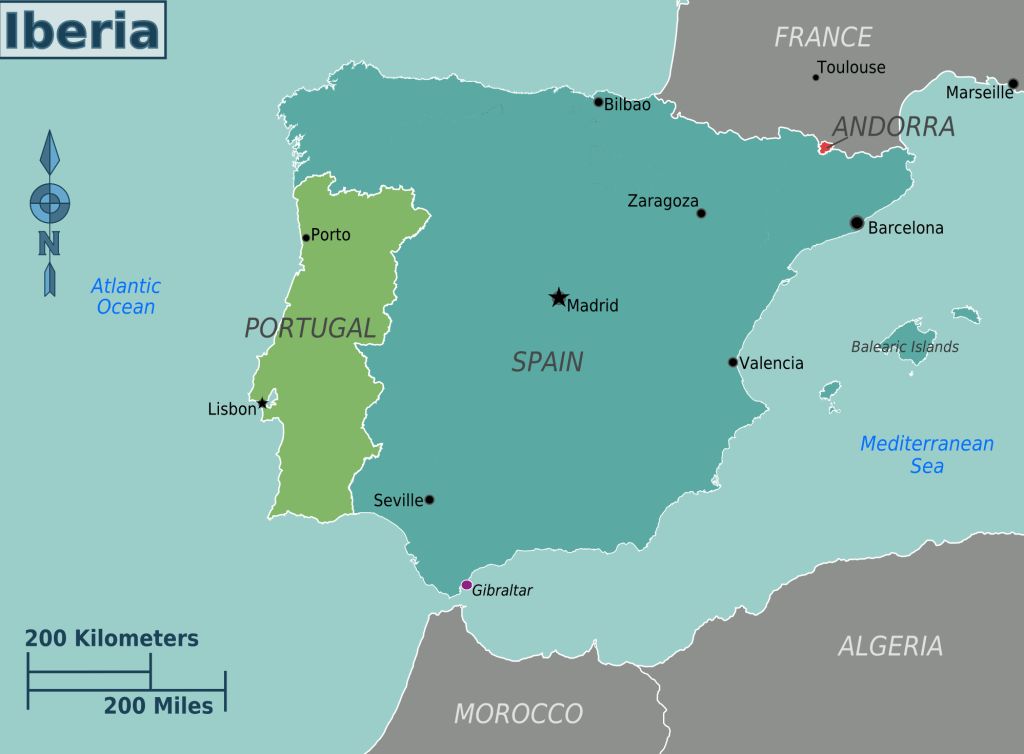
4. Iberian Peninsula
Location: Southwest Europe
Countries: Spain, Portugal, Andorra
Features: Pyrenees Mountains, fertile plains of Andalusia, Meseta Central plateau, and historic cities like Madrid and Lisbon.
5. Italian Peninsula
Location: Southern Europe
Countries: Italy, Vatican City, San Marino
Features: Apennine Mountains, fertile Po Valley, Mediterranean coastline, and iconic landmarks like the Colosseum and Vatican City.

6. Balkan Peninsula
Location: Southeast Europe
Countries: Greece, Albania, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Croatia, Montenegro, Serbia, Kosovo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Romania, Slovenia
Features: Dinaric Alps, Balkan Mountains, Adriatic and Aegean coastlines, and rich cultural heritage.

7. Kamchatka Peninsula
Location: Far East Russia
Features: Volcanic peaks, geothermal springs, pristine wilderness, and diverse wildlife including brown bears and salmon.

8. Yucatán Peninsula
Location: Mexico
Features: Ancient Mayan ruins, limestone sinkholes (cenotes), Caribbean coastline, and the biodiverse Sian Ka’an Biosphere Reserve.

9. Alaska Peninsula
Location: United States (Alaska)
Features: Aleutian Range volcanoes, Kodiak Island, Bristol Bay, and abundant wildlife including grizzly bears and bald eagles.

10. Scandinavian Peninsula
Location: Northern Europe
Countries: Norway, Sweden
Features: Fjords, boreal forests, Arctic tundra, and vibrant cities like Oslo and Stockholm.

You May Also Like

