The Atlantic Ocean, spanning over 106.5 million square kilometers, is the second-largest ocean on Earth, stretching from the Arctic in the north to the Antarctic in the south. The Atlantic Ocean, named after the mythical Atlas of Greek mythology, is one of the world’s major oceans, spanning the distance between the Americas to the west and Europe and Africa to the east. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Southern Ocean to the south, and the continents of North and South America, Europe, and Africa.
History of the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean has played a pivotal role in shaping human history, facilitating exploration, trade, and cultural exchange across continents and civilizations. From ancient seafaring voyages to modern maritime endeavors, the Atlantic has been a conduit for adventure, conquest, and discovery.
Ancient civilizations such as the Phoenicians, Greeks, and Romans ventured into the Atlantic Ocean in search of new lands, resources, and trade routes. The Phoenician sailors, renowned for their navigational skills, explored the western Mediterranean and may have ventured beyond the Strait of Gibraltar into the Atlantic. The Age of Exploration, spanning the 15th to the 17th centuries, witnessed a surge in maritime expeditions across the Atlantic Ocean. European powers such as Portugal, Spain, England, and France embarked on voyages of discovery, seeking new trade routes to Asia, Africa, and the Americas.
Some Interesting facts about Atlantic Ocean
1. Size and Depth
The Atlantic Ocean covers approximately 20% of the Earth’s surface area, making it the second-largest ocean after the Pacific. Its vastness extends across diverse climates, ecosystems, and geological features, ranging from the icy waters of the Arctic to the warm currents of the Caribbean.
2. Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Running through the center of the Atlantic Ocean is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a massive underwater mountain range that stretches for over 16,000 kilometers. This geological feature marks the boundary between the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates in the northern Atlantic and the South American and African plates in the southern Atlantic.
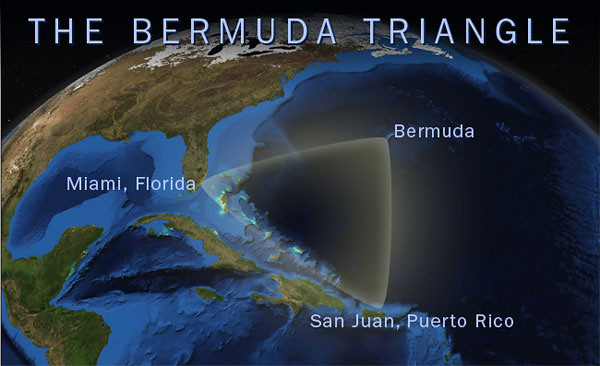
3. Bermuda Triangle
The Bermuda Triangle, located in the western part of the North Atlantic Ocean, has captured the imagination of explorers and storytellers for centuries. Also known as the Devil’s Triangle, this mysterious region is infamous for the disappearance of numerous ships and aircraft under unexplained circumstances.
4. Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream is a powerful ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows along the eastern coast of North America before crossing the Atlantic Ocean towards Europe. This warm current influences weather patterns, ocean circulation, and marine life along its path, playing a crucial role in shaping regional climates and ecosystems.
5. Marine Biodiversity
The Atlantic Ocean is home to a rich diversity of marine life, including whales, dolphins, sharks, sea turtles, and countless species of fish, crustaceans, and invertebrates. Its diverse habitats, from coral reefs to deep-sea trenches, support a wide range of organisms adapted to various environmental conditions.
6. Sargasso Sea
Located in the North Atlantic Ocean, the Sargasso Sea is a unique marine ecosystem characterized by its calm, clear waters and floating mats of Sargassum seaweed. This distinctive habitat provides shelter and food for a variety of marine species, including fish, turtles, and invertebrates.
7. Titanic Wreckage
The Atlantic Ocean is the final resting place of the RMS Titanic, the legendary ocean liner that sank on its maiden voyage in 1912 after striking an iceberg. The wreckage of the Titanic was discovered in 1985 by oceanographer Robert Ballard, lying over 3,800 meters below the surface of the North Atlantic.
8. Underwater Volcanoes
The Atlantic Ocean is dotted with underwater volcanoes and seamounts, some of which rise thousands of meters from the ocean floor. These volcanic features are associated with the movement of tectonic plates and the formation of new oceanic crust along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
9. Ocean Currents and Climate
Ocean currents play a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate by redistributing heat and moisture around the globe. The Atlantic Ocean is traversed by a complex system of currents, including the North Atlantic Drift, the Canary Current, and the Equatorial Counter Current, which influence weather patterns and climate variability in the region.
10. Historical Significance
The Atlantic Ocean has been a vital conduit for trade, exploration, and cultural exchange throughout human history. From the voyages of Christopher Columbus to the transatlantic slave trade, the Atlantic has shaped the destinies of nations and civilizations, leaving indelible marks on the course of human events.
11. Fishing and Maritime Industries
The Atlantic Ocean supports lucrative fishing and maritime industries, providing vital resources and livelihoods for coastal communities around the world. Commercial fisheries harvest a wide variety of seafood from the Atlantic, including cod, haddock, tuna, and shrimp, contributing to global food security and economic prosperity.
12. Climate Change and Ocean Acidification
The Atlantic Ocean is experiencing the impacts of climate change and ocean acidification, including rising sea levels, warming temperatures, and shifting marine ecosystems. These changes pose significant challenges for marine life, coastal communities, and vulnerable ecosystems dependent on stable environmental conditions.
FAQs about the Atlantic Ocean
1. What is the Atlantic Ocean’s average depth?
The average depth of the Atlantic Ocean is approximately 3,646 meters (11,962 feet). However, the ocean’s depth varies significantly across different regions, with the deepest point, known as the Milwaukee Deep in the Puerto Rico Trench, reaching depths of over 8,376 meters (27,480 feet).
2. How many countries border the Atlantic Ocean?
The Atlantic Ocean borders numerous countries across four continents: North America, South America, Europe, and Africa. Over 90 countries have coastlines along the Atlantic Ocean, including the United States, Canada, Brazil, the United Kingdom, France, Spain, Portugal, South Africa, and Nigeria, among others.
3. What is the temperature range of the Atlantic Ocean?
The temperature of the Atlantic Ocean varies depending on factors such as latitude, season, and ocean currents. In tropical regions near the equator, surface temperatures can exceed 25°C (77°F), while in polar regions near the poles, temperatures may remain near freezing. The Gulf Stream and North Atlantic Drift influence temperature patterns in the North Atlantic, maintaining warmer waters along the eastern coast of North America and western Europe.
4. How is the Atlantic Ocean connected to other oceans?
The Atlantic Ocean is connected to the Arctic Ocean through the Greenland Sea and the Labrador Sea in the north. It is connected to the Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, through the Drake Passage and the Southern Atlantic Ocean. Additionally, the Atlantic Ocean is connected to the Indian Ocean through the Southern Ocean, and to the Pacific Ocean through the Strait of Magellan, the Panama Canal, and the Drake Passage.
5. What are some of the major ports located along the Atlantic Ocean?
The Atlantic Ocean is home to numerous major ports that serve as vital hubs for trade, commerce, and transportation. Some of the notable ports include New York/New Jersey (United States), Rotterdam (Netherlands), Hamburg (Germany), Rio de Janeiro (Brazil), Cape Town (South Africa), and Lagos (Nigeria).
6. What are the primary threats to the health of the Atlantic Ocean?
The Atlantic Ocean faces a range of environmental challenges, including overfishing, habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and ocean acidification. These threats can impact marine ecosystems, biodiversity, and coastal communities, highlighting the need for sustainable management and conservation efforts.
7. How does the Atlantic Ocean influence global climate patterns?
The Atlantic Ocean plays a significant role in regulating global climate patterns through its ocean currents, which transport heat and moisture between different regions of the world. The Gulf Stream, for example, warms the climate of western Europe, while the North Atlantic Oscillation affects weather patterns in the North Atlantic region. Changes in Atlantic Ocean circulation can have far-reaching impacts on weather, precipitation, and sea level rise around the world.
You May Also Like

