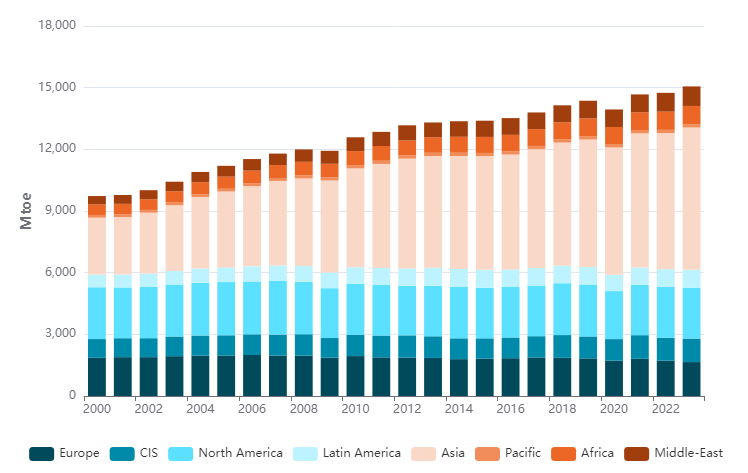
Global energy consumption witnessed a significant shift in 2023, with overall usage increasing by 2.2%, marking a sharp rise from the average annual growth rate of 1.5% recorded during the pre-pandemic decade (2010-2019). This growth is attributed to dynamic energy trends across regions, with developing economies showing accelerated consumption rates and developed nations focusing on sustainability and efficiency. The data, sourced from Enerdata’s 2023 Global Energy Report, sheds light on the evolving global energy landscape and its implications for a sustainable future.
A New Growth Phase for Global Energy Consumption
In a world recovering from pandemic disruptions, the 2.2% growth in energy consumption highlights renewed industrial activity, urbanization, and energy demands. The report indicates that emerging economies, particularly the BRICS nations (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa), were at the forefront of this surge, contributing 42% of the world’s total energy consumption.
China, the largest energy consumer globally, recorded a remarkable 6.6% increase in energy usage, doubling its growth rate compared to the previous decade. India followed with a 5.1% rise, reflecting its expanding industrial base and growing population demands. Brazil’s energy consumption also rose by 3.3%, a significant jump from its historical annual average of 0.9%. Meanwhile, Russia’s energy growth was negligible at 0.3%, and South Africa saw a decline of 1.2%, largely due to persistent supply issues and infrastructure challenges.
Regional Trends: The Middle East and Emerging Economies
The Middle East emerged as another high-growth region, with energy consumption increasing by 3.7%. Iran and the United Arab Emirates played significant roles in this growth, leveraging their natural resource wealth and increasing domestic energy demands.
In Asia, emerging economies such as Vietnam, Indonesia, and the Philippines saw strong growth in energy consumption, driven by industrialization and expanding manufacturing sectors. These nations are becoming key players in global energy dynamics as they balance economic growth with sustainable practices.
Energy Decline in OECD Nations: A Focus on Efficiency
In contrast to the consumption growth in developing regions, OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) countries experienced a 1.5% decline in energy use, marking the second consecutive year of reduction. This trend reflects the emphasis these countries are placing on energy efficiency and renewable energy adoption.
The European Union (EU) stood out with a significant 4.2% drop in energy consumption. Germany, Europe’s largest economy, saw a drastic 9.3% decline, attributed to increased energy efficiency measures, reduced industrial output, and a shift towards renewable energy sources. Similarly, Japan and South Korea recorded reductions of 3.5% and 2.8%, respectively.
The United States maintained steady energy consumption levels, with minor adjustments between different energy sectors. While oil consumption for transportation rose, electricity demand for cooling decreased due to milder weather. The U.S. also saw a continued decline in coal usage, reflecting its shift toward cleaner energy sources.
Renewables and Climate Commitments at COP28
The 2023 report highlights the growing role of renewable energy in shaping global consumption patterns. During COP28, over 120 countries pledged to triple renewable energy capacity to 11,000 GW by 2030. Additionally, nations committed to doubling the rate of energy efficiency improvements from the current 2% annually to 4%.
While these commitments signal a strong global consensus toward addressing climate change, achieving these goals will require substantial investments in renewable energy technologies, infrastructure upgrades, and supportive policies. The role of solar, wind, and hydropower will be critical in this transition, particularly in regions like India and China, which are investing heavily in renewable capacity.
Challenges in Balancing Growth and Sustainability
Despite the promising growth of renewables, several challenges remain. Emerging economies are grappling with increasing energy demands, often relying on fossil fuels to meet immediate needs. In contrast, developed nations face the high costs of transitioning from legacy systems to sustainable energy solutions.
For instance, South Africa’s decline in energy consumption highlights the consequences of inadequate infrastructure and unreliable supply chains. Similarly, Russia’s stagnant energy growth highlights the geopolitical and economic pressures affecting energy distribution and consumption.
The Role of Energy Efficiency in Shaping the Future
Energy efficiency emerged as a key theme in the 2023 report. The decline in energy consumption across OECD countries highlights the impact of efficiency measures and advanced technologies. Smart grids, energy storage solutions, and digital tools for monitoring and optimizing energy usage are becoming increasingly prevalent.
The report also emphasizes the need for energy efficiency in sectors like transportation and manufacturing, where substantial energy savings can be achieved. Electrification of transportation, coupled with advancements in battery technology, is expected to play a significant role in reducing oil dependency.
The Path Ahead: Achieving a Sustainable Energy Future
The 2023 energy trends illustrate a world at a crossroads. On one hand, the growth in energy consumption highlights the challenges of meeting global energy demands while addressing climate change. On the other hand, the rise of renewables and efficiency measures offers a pathway toward sustainability.
Achieving the ambitious targets set during COP28 will require global cooperation, robust policy frameworks, and significant investments in research and development. Key players like China and India will need to balance their rapid growth with sustainability goals, while developed nations must continue to lead by example in renewable adoption and efficiency improvements.
Conclusion
The 2023 Enerdata report paints a vivid picture of global energy dynamics, highlighting both the challenges and opportunities in the journey toward a sustainable energy future. The transition to a sustainable energy future is not without hurdles, but with collective action and innovative solutions, a balance between energy demands and climate goals can be achieved.

