Have you ever heard of an atmospheric river storm? It might sound like something out of a science fiction movie, but it’s a real phenomenon that plays a crucial role in shaping our weather patterns and influencing regional climates. Let us check out and explore what they are, how they form, and why they matter.
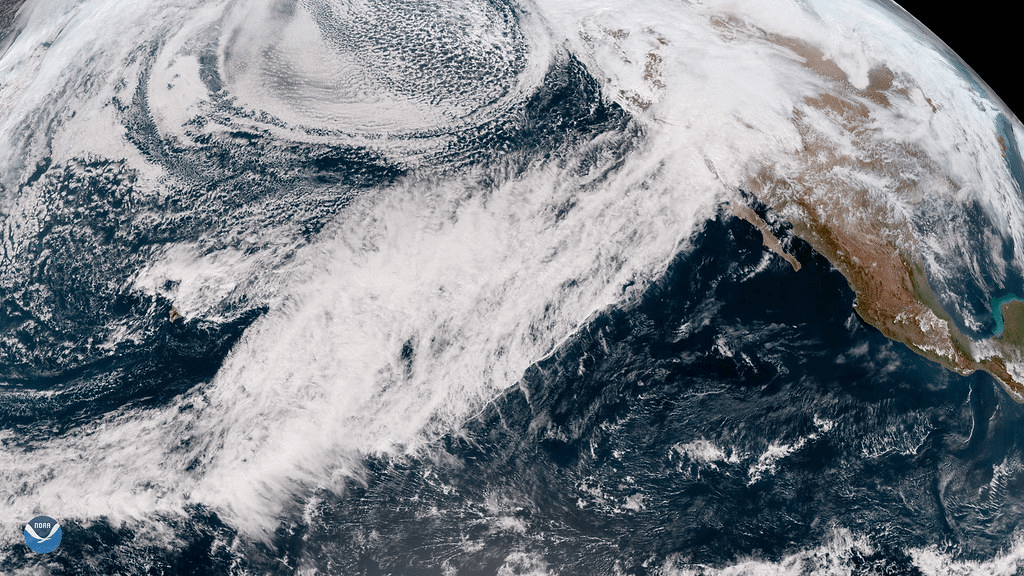
Understanding Atmospheric Rivers
Atmospheric rivers are long, narrow corridors of concentrated moisture in the atmosphere that transport large amounts of water vapor across vast distances. These atmospheric rivers can extend thousands of kilometers from the tropics to higher latitudes and can carry as much water as several times the flow of the Amazon River!
Think of atmospheric rivers as giant “rivers in the sky” that ferry moisture from one part of the world to another. They play a vital role in the Earth’s water cycle, delivering much-needed precipitation to regions experiencing drought while also fueling intense storms and flooding events.
Formation of Atmospheric River Storms
So, how do atmospheric river storms form? It all starts with the interaction between warm ocean waters and the atmosphere. In tropical and subtropical regions, where sea surface temperatures are relatively high, water evaporates from the ocean surface, creating a reservoir of moisture in the air.
As warm, moist air rises and moves poleward, it encounters atmospheric features such as jet streams and low-pressure systems, which steer and channel the moisture-laden air into narrow bands known as atmospheric rivers. These corridors of moisture can extend for thousands of kilometers across oceans and continents, bringing rain, snow, and wind to the regions they traverse.
Where Do They Form?
Atmospheric rivers crisscross the globe, most commonly in the mid-latitudes. They emerge over warm waters, often tropical oceans, guided by low-level jet streams. Along the U.S. West Coast, the Pacific Ocean serves as their moisture reservoir. As they hit the coastal mountain ranges and the Sierra Nevada, they release that water reservoir, drenching the land.
Characteristics of Atmospheric River Storms
Atmospheric river storms can vary in intensity and duration, ranging from weak, transient events to powerful, long-lasting systems. Some key characteristics of atmospheric river storms include:
- Heavy Precipitation: Atmospheric river storms are capable of producing significant amounts of precipitation, including rain, snow, and ice, over large areas. When these moisture-laden air masses encounter mountains or other topographic barriers, they can unleash intense rainfall or heavy snowfall, leading to flooding, landslides, and avalanches.
- Strong Winds: Along with precipitation, atmospheric river storms can generate strong winds, especially along coastlines and in mountainous regions. Wind gusts associated with atmospheric river storms can reach hurricane force, causing damage to structures, trees, and power lines.
- Warm Temperatures: Atmospheric river storms often bring milder temperatures to regions experiencing their effects, particularly during the winter months. The influx of warm, moist air can raise temperatures above seasonal norms, leading to rapid snowmelt, increased runoff, and heightened flood risk.
- Snowfall in Mountainous Areas: In regions with high elevations, such as the western United States and the European Alps, atmospheric river storms can deposit heavy snowfall in mountainous areas. This snowpack serves as a critical water resource, providing freshwater supplies for drinking, irrigation, and hydroelectric power generation during the dry summer months.
Impacts of Atmospheric River Storms
The impacts of atmospheric river storms can be far-reaching and profound, affecting both human communities and natural ecosystems. Some common impacts of atmospheric river storms include:
- Flooding: Atmospheric river storms can trigger flash floods, river floods, and coastal flooding, especially in areas with poor drainage systems or vulnerable infrastructure. Heavy rainfall combined with melting snow can overwhelm rivers and streams, leading to rapid rises in water levels and inundation of floodplains.
- Landslides and Mudslides: The combination of saturated soils and steep terrain can increase the risk of landslides and mudslides during and after atmospheric river storms. These mass movements of soil and rock can bury roads, homes, and vegetation, posing hazards to human life and property.
- Water Supply: Atmospheric river storms play a critical role in replenishing water supplies, particularly in regions dependent on snowpack for freshwater resources. Snowfall in mountainous areas contributes to reservoir storage and groundwater recharge, supporting agricultural, industrial, and municipal water needs.
- Ecological Impacts: Atmospheric river storms can have both positive and negative impacts on natural ecosystems. While they provide much-needed moisture to support plant growth and wildlife habitats, they can also cause habitat destruction, soil erosion, and changes in streamflow regimes that affect aquatic organisms and riparian ecosystems.
The Trouble of Consecutive Storms
The consecutive atmospheric rivers, known as AR families, can spell trouble. The first storm saturates the ground, leaving it unable to absorb more water. As subsequent storms arrive, rivers swell, streams overflow, and the risk of flooding soars. Add snowmelt from warm temperatures, and you’ve got a recipe for disaster.
In December 2022 and January 2023, California had nine strong atmospheric rivers in a row. These heavy rains tested the state’s strength and showed how nature can be generous and fierce at the same time.
Monitoring and Forecasting Atmospheric River Storms
Given the significant impacts of atmospheric river storms, scientists and meteorologists employ a variety of tools and techniques to monitor and forecast these weather events. Satellite imagery, weather radar, and atmospheric models provide valuable data on the location, intensity, and movement of atmospheric rivers, helping forecasters issue timely warnings and advisories to communities at risk.
In regions prone to atmospheric river storms, such as the West Coast of the United States and western Europe, government agencies and emergency management organizations work closely with the public to prepare for potential impacts, including flooding, landslides, and power outages. Preparedness measures may include flood control infrastructure, evacuation plans, and public education campaigns on flood safety and emergency preparedness.
References:
- https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/what-are-atmospheric-rivers-and-how-are-they-changing/
- https://www.britannica.com/science/storm
You May Also Like

