Water is essential for life on Earth, and access to clean, fresh water is a fundamental human need. However, many regions around the world suffer from water scarcity, making it challenging to meet the demands of growing populations. Desalination, the process of removing salt and other impurities from seawater, has emerged as a vital solution to address this pressing issue. In this article, we will explore the science behind desalination, its various methods, environmental impacts, and its role in securing a sustainable water supply for the future.
Understanding the Need for Desalination
Freshwater makes up only a small fraction of Earth’s total water resources, with approximately 97.5% of water on our planet found in oceans and seas, making it salty and unfit for consumption or agricultural use. The remaining 2.5% is freshwater, but a significant portion of that is locked in ice caps and glaciers. This leaves a relatively minuscule portion of freshwater available for human use.
Rapid population growth, industrialization, and climate change have exacerbated water scarcity in many regions, leading to increased competition for limited freshwater resources. As a result, the need for alternative sources of freshwater, such as desalination, has become increasingly important.
The Science of Desalination
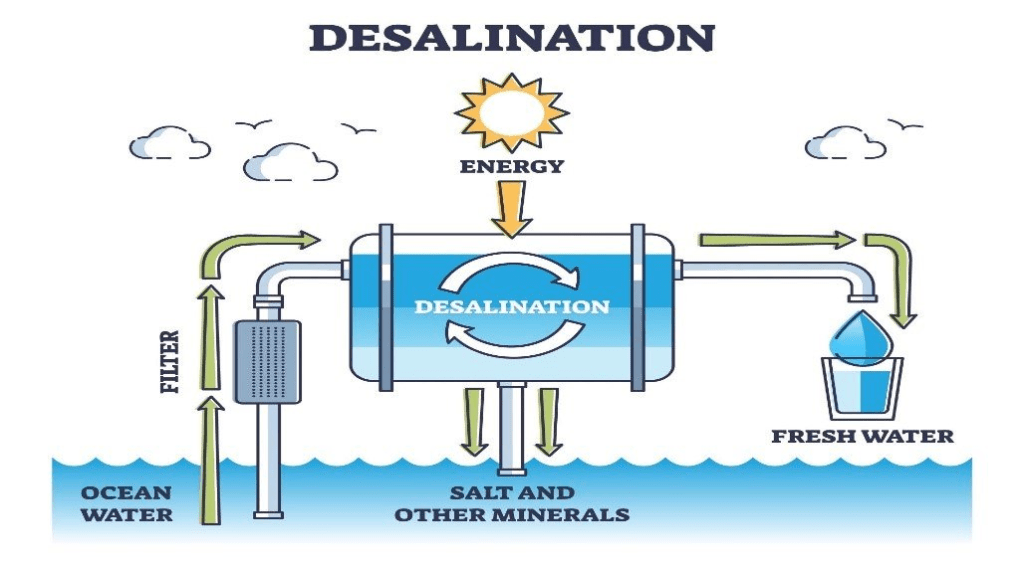
Desalination relies on the principles of physical and chemical separation to remove salt and impurities from seawater, making it suitable for various uses. The two primary methods of desalination are distillation and membrane processes.
Distillation
Distillation is one of the oldest methods of desalination. It mimics the natural water cycle by heating seawater to create water vapor, which is then condensed back into liquid form. The condensed vapor, or freshwater, is collected, leaving behind the concentrated brine solution. This process effectively separates freshwater from salt and other impurities.
Membrane Processes
Membrane processes, including reverse osmosis and electrodialysis, are the most common methods of desalination today. These processes rely on semi-permeable membranes that allow water molecules to pass through while blocking the passage of salts and other contaminants.
- Reverse Osmosis: In reverse osmosis, high pressure is applied to seawater, forcing it through a membrane that separates the freshwater from the concentrated brine. This method is highly efficient and widely used for desalination.
- Electrodialysis: Electrodialysis uses an electric field to drive the movement of ions through selective ion-exchange membranes. This separates the salt ions from the water, resulting in freshwater.
Also Read: SUSTAINABLE TECHNOLOGIES FOR WATER SCARCITY
Methods of Desalination: Pros and Cons
Each desalination method has its advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different circumstances and locations.
Advantages of Desalination:
- Reliable Source of Freshwater: Desalination provides a consistent and reliable source of freshwater, regardless of weather conditions or climate.
- Drought Resilience: Desalination can help regions cope with droughts and water shortages by supplementing traditional water sources.
- Reduces Pressure on Freshwater Supplies: By tapping into seawater resources, desalination can reduce the stress on existing freshwater sources, preserving them for other essential uses.
Disadvantages of Desalination:
- High Energy Consumption: Desalination processes, especially reverse osmosis, require a significant amount of energy, which can be expensive and contribute to carbon emissions.
- Environmental Impacts: The disposal of concentrated brine into the sea can harm marine ecosystems, and the intake of seawater during the desalination process may harm aquatic life.
- Cost: Building and maintaining desalination plants can be expensive, which can make the resulting freshwater relatively costly.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Desalination, while providing a valuable source of freshwater, can have significant environmental impacts. One of the most concerning issues is the disposal of concentrated brine back into the ocean. The brine is denser than seawater and contains elevated salt levels, which can harm marine life and ecosystems near the discharge point. To mitigate these impacts, researchers are exploring ways to dilute and disperse brine more effectively.
Additionally, the energy requirements of desalination contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Developing more energy-efficient desalination technologies and incorporating renewable energy sources can help reduce the carbon footprint of desalination plants.
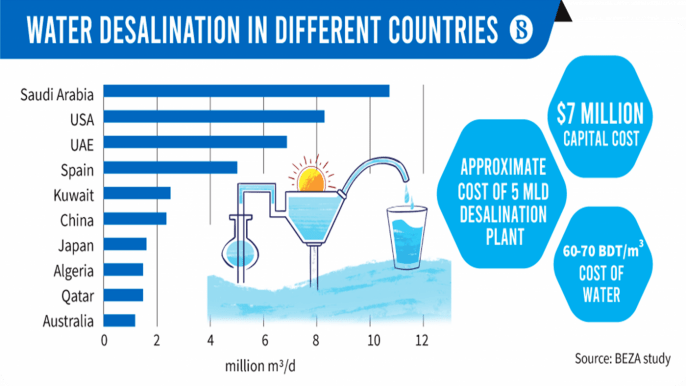
Desalination Around the World
Desalination is not a new concept, but its use has grown significantly in recent decades, especially in regions facing chronic water shortages. Some of the world’s largest desalination plants are located in countries such as Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Israel, where freshwater resources are scarce.
Also Read: TOP 10 COUNTRIES FACING THE EXTREME WATER STRESS
The expansion of desalination capacity has not been limited to arid regions. Coastal cities in the United States, including Los Angeles and San Diego, have invested in desalination as a way to diversify their water supply portfolios and improve water resilience.
Future of Desalination
As the global demand for freshwater continues to rise, desalination will likely play an increasingly important role in meeting these demands. Researchers are actively working to address the challenges associated with desalination, including reducing energy consumption, minimizing environmental impacts, and making the process more cost-effective.
One promising avenue of research is the development of innovative materials for membranes that can improve desalination efficiency and reduce energy requirements. Additionally, advancements in renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, offer the potential to power desalination plants sustainably.
Top desalination plants
Desalination plants are critical for providing fresh water in regions facing water scarcity. Here are some of the top desalination plants from around the world:
- Sorek Desalination Plant (Israel): The Sorek plant is one of the world’s largest and most efficient desalination facilities. It uses reverse osmosis technology to produce about 150 million cubic meters (39.6 billion gallons) of freshwater annually, serving approximately 20% of Israel’s municipal water demand.
- Ras Al Khair Desalination Plant (Saudi Arabia): Located on the Arabian Gulf, the Ras Al Khair plant is one of the largest desalination facilities in the world. It utilizes both multi-stage flash distillation and reverse osmosis technologies to produce over 1 million cubic meters (264 million gallons) of freshwater per day.
- Al Shuqaiq Desalination Plant (Saudi Arabia): This plant is another major desalination facility in Saudi Arabia, producing around 212,000 cubic meters (56 million gallons) of freshwater per day using reverse osmosis technology.
- Carlsbad Desalination Plant (United States): Located in California, the Carlsbad plant is the largest desalination facility in the Western Hemisphere. It uses reverse osmosis to produce approximately 190,000 cubic meters (50 million gallons) of freshwater per day, providing a significant water supply for the San Diego area.
- Jebel Ali Desalination Plant (United Arab Emirates): Situated in Dubai, this plant is one of the oldest and largest desalination facilities in the UAE. It has a capacity of around 300,000 cubic meters (79 million gallons) of freshwater per day and uses multi-stage flash distillation technology.
- Tampa Bay Seawater Desalination Plant (United States): Located in Florida, this reverse osmosis facility provides up to 95 million liters (25 million gallons) of freshwater per day to the Tampa Bay region, helping to meet the area’s freshwater needs during dry spells.
- Tianjin Dagang Desalination Plant (China): The Tianjin Dagang plant is one of the largest desalination facilities in China, producing approximately 200,000 cubic meters (52 million gallons) of freshwater per day using reverse osmosis technology.
- Honolulu Seawater Desalination Plant (United States): This plant on the island of Oahu in Hawaii uses reverse osmosis to produce freshwater from seawater. It contributes to the island’s water supply and helps reduce reliance on groundwater sources.
Also Read: IS WATER RENEWABLE OR NON-RENEWABLE RESOURCE?
Final Words
Desalination is a vital technology for addressing water scarcity challenges in a world where freshwater resources are under increasing pressure. By harnessing the principles of separation and purification, desalination processes provide a source of freshwater from the abundant reserves of seawater. However, it is essential to balance the benefits of desalination with its environmental and economic costs. Continued research and innovation in desalination technology, along with sustainable practices, can help secure a reliable source of freshwater for future generations while minimizing the impact on our planet’s ecosystems.
You May Also Like

