The rainforest is a mesmerizing wonder of nature, teeming with life and beauty. One of the most remarkable features of this ecosystem is its unparalleled biodiversity. In this article, we will explore the diverse and fascinating life forms that call the rainforest their home, emphasizing the importance of preserving this unique environment.
A Myriad of Plant Species
The rainforest boasts an astonishing array of plant species. From towering trees that reach for the sky to tiny mosses hidden on the forest floor, each species plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of this ecosystem. Not only do these plants provide a habitat for countless animals, but they also serve as sources of medicine, food, and even contribute to regulating our planet’s climate. While it is practically impossible to list all the plant species found in rainforests, here are some notable examples:
Tropical Trees:
- Brazil Nut Tree (Bertholletia excelsa): Known for producing large, hard-shelled nuts containing edible seeds.
- Kapok Tree (Ceiba pentandra): Recognized for its massive size and fluffy seed fibers, used as stuffing for pillows and mattresses.
- Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis): The primary source of natural rubber, obtained from its latex.
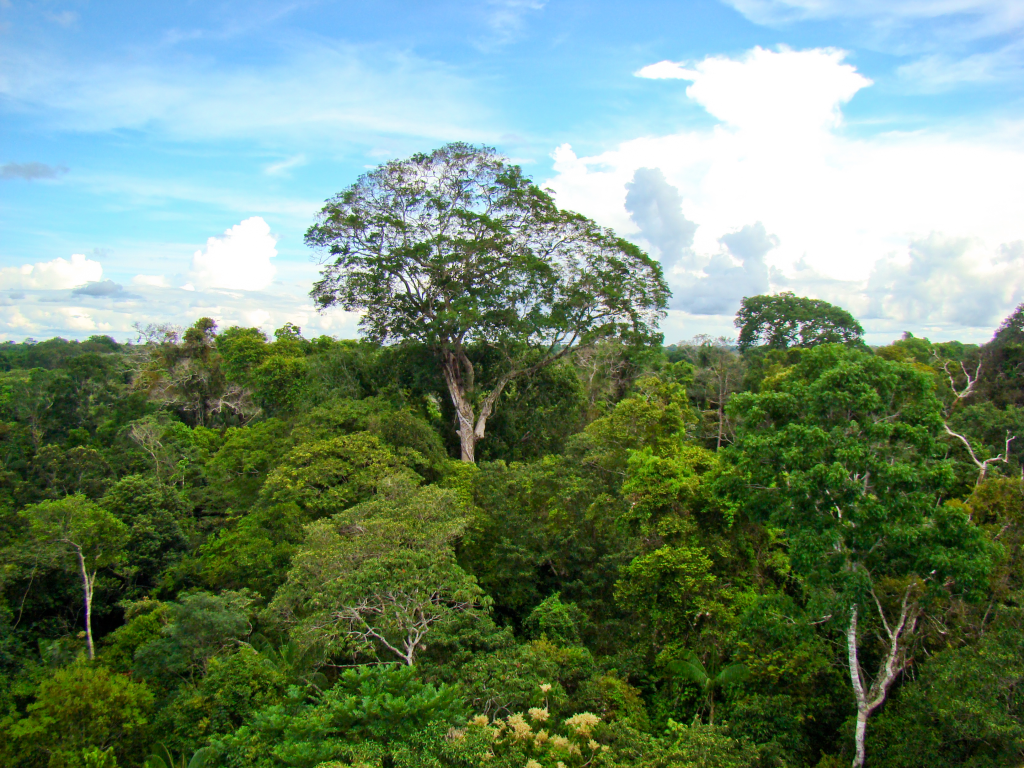

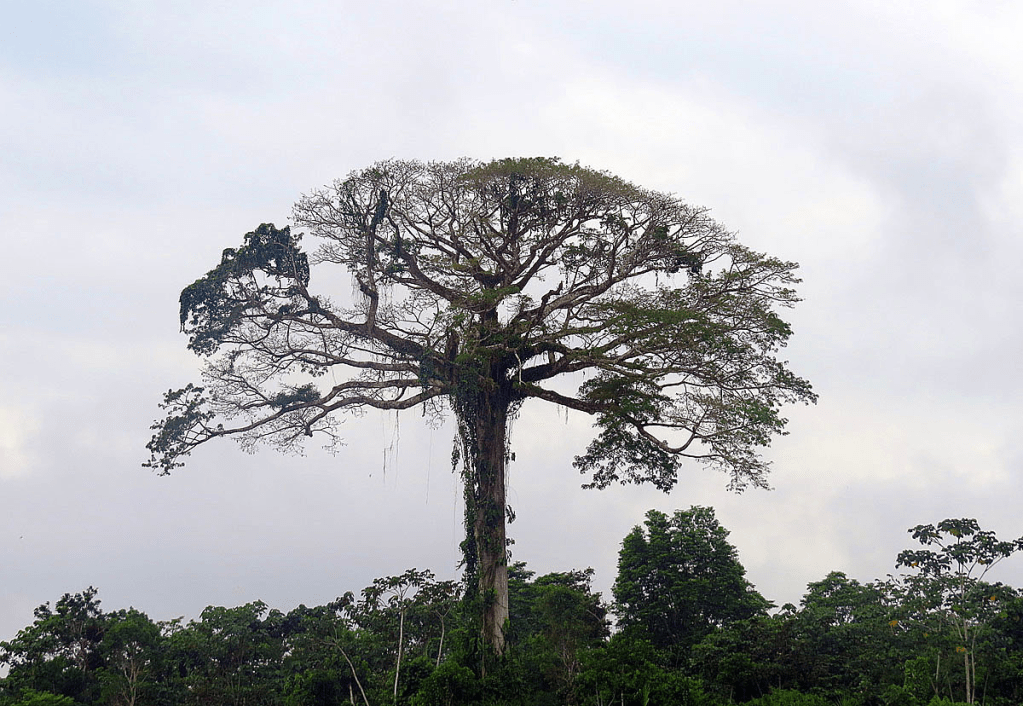
Epiphytes:
- Orchids: A vast variety of orchid species thrive in rainforests, known for their vibrant and intricate flowers.
- Bromeliads: These plants gather water in their central cups, providing habitats for various animals in the rainforest canopy.
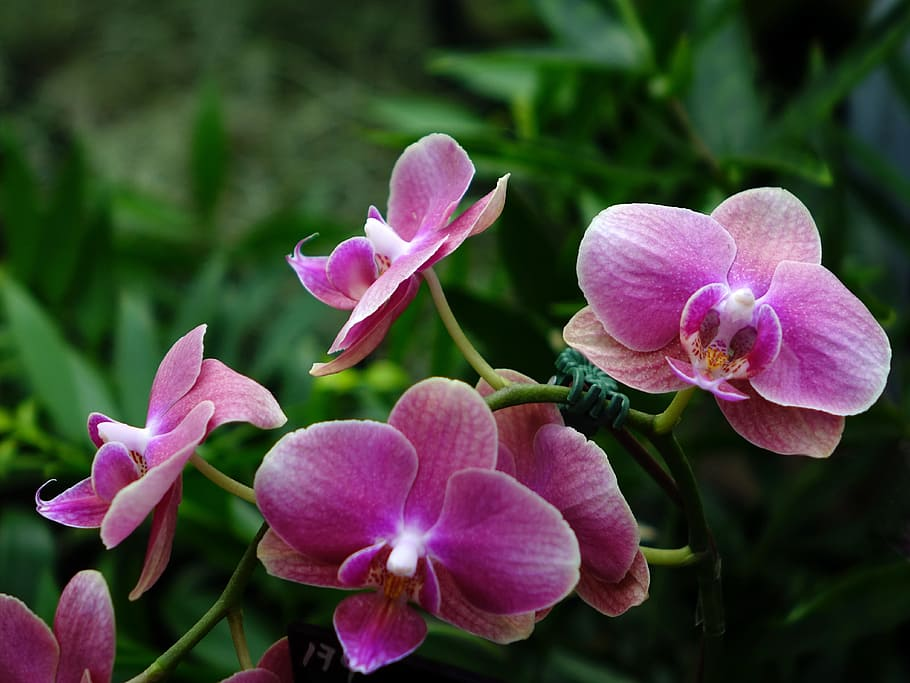
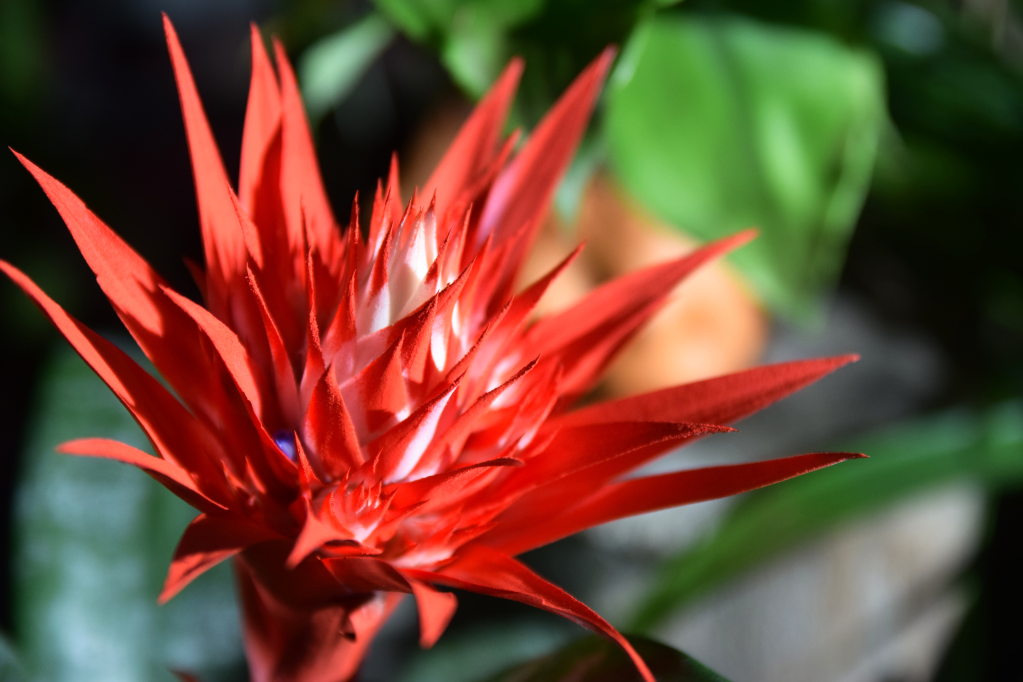


Medicinal Plants:
- Cinchona Tree (Cinchona officinalis): The source of quinine, a compound used to treat malaria.
- Curare Vine (Chondrodendron tomentosum): Used by indigenous people to make curare poison, historically used for hunting and medicinal purposes.
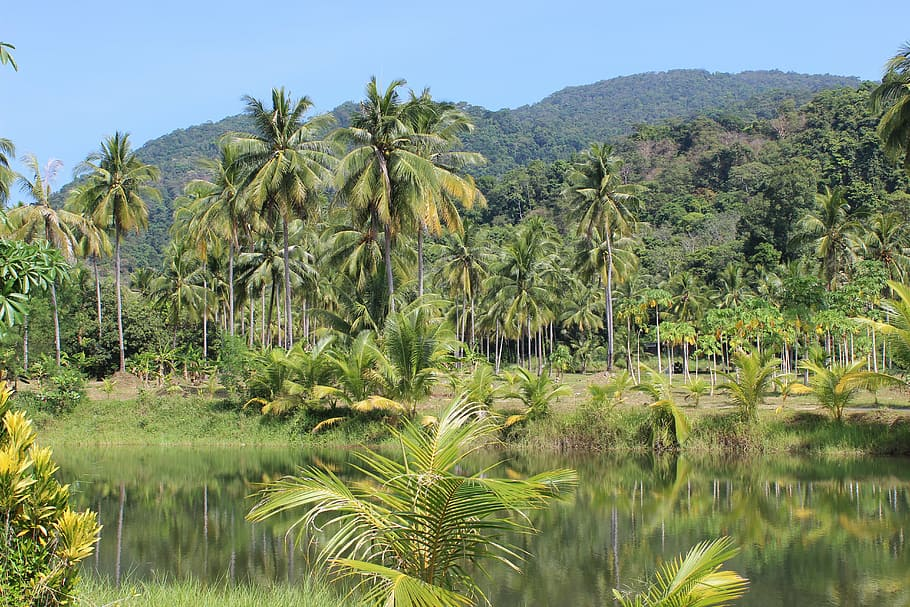
Palms:
- Açaí Palm (Euterpe oleracea): Produces açaí berries, which have gained popularity as a superfood.
- Coconut Palm (Cocos nucifera): Known for its versatile uses and providing coconut water, milk, and oil.


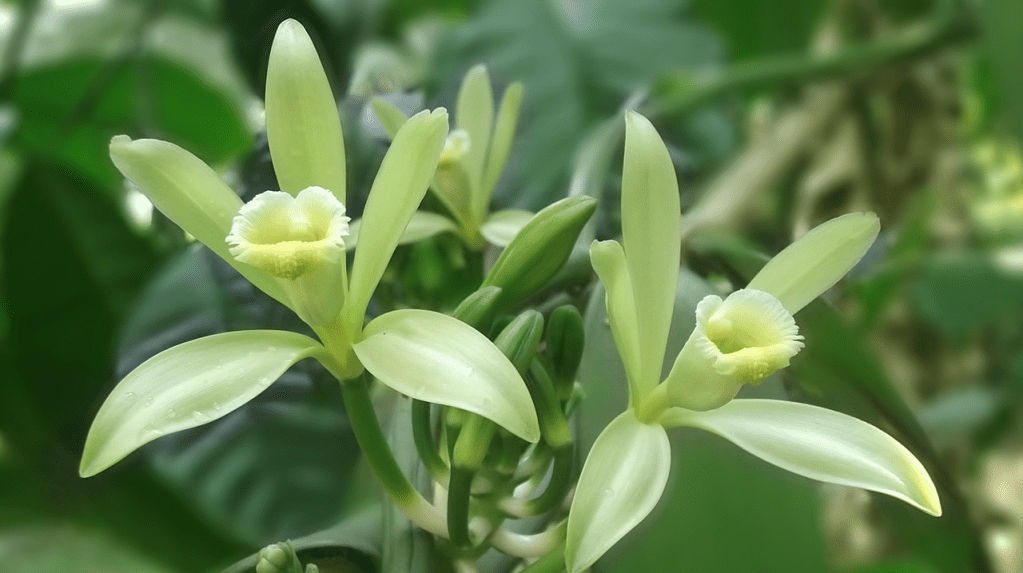
Climbers and Vines:
- Passionflower (Passiflora spp.): Known for their exquisite flowers and fruit, including passion fruit.
- Vanilla Orchid (Vanilla planifolia): The source of vanilla flavoring, derived from its seed pods.
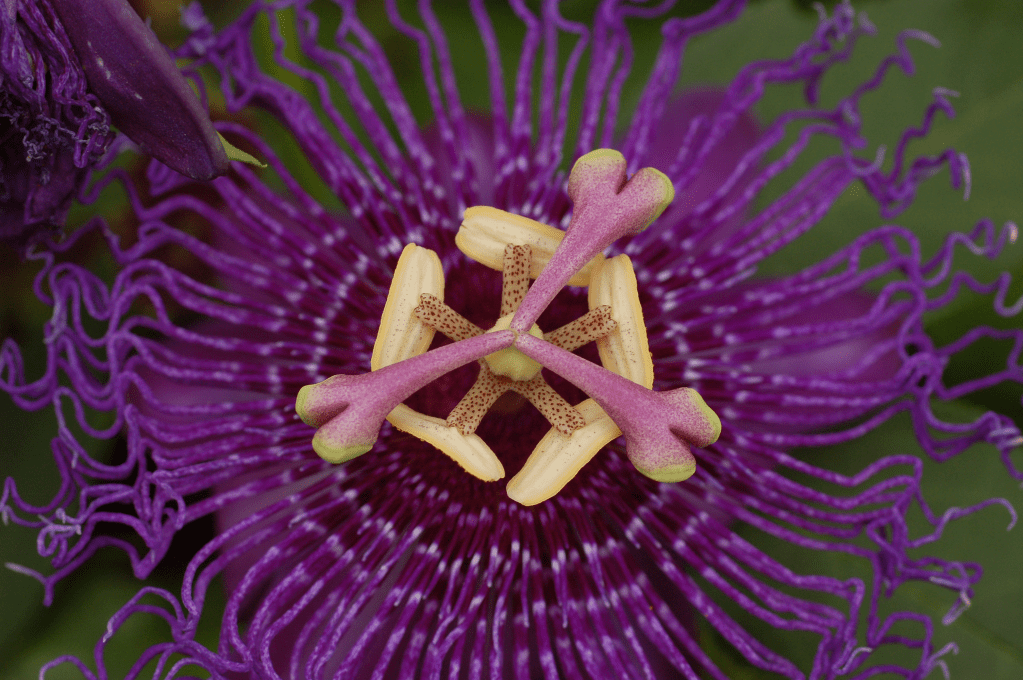

Medicinal Trees and Plants:
- Cat’s Claw (Uncaria tomentosa): Known for its potential medicinal properties, including immune system support.
- Ylang-Ylang Tree (Cananga odorata): Source of essential oil used in aromatherapy.
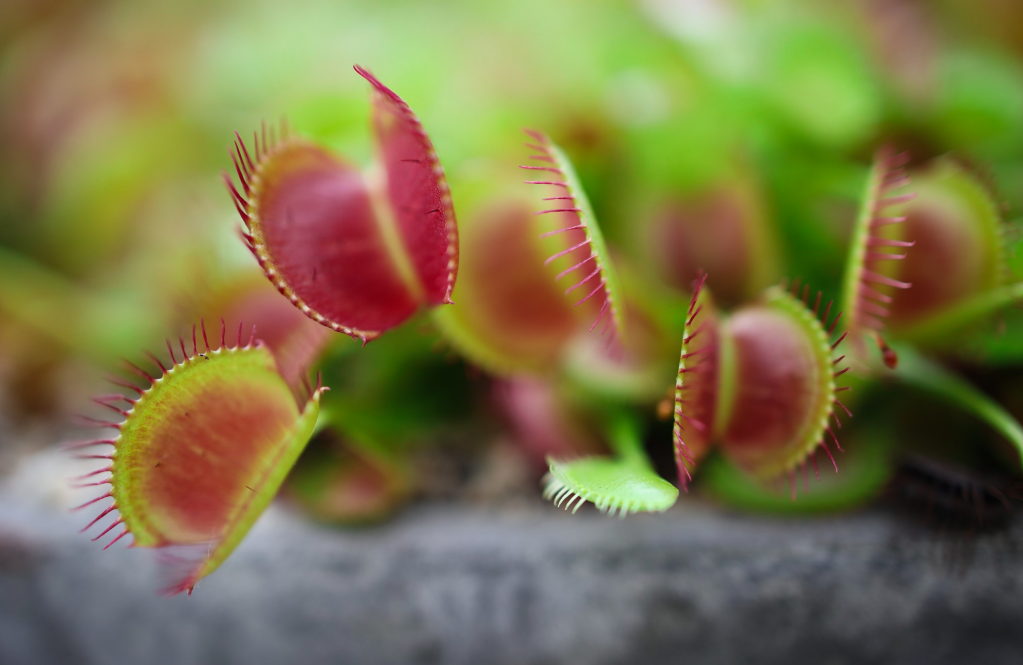
Carnivorous Plants:
- Venus Flytrap (Dionaea muscipula): A well-known carnivorous plant with hinged trap leaves that capture insects.

The Wonders of Animal Diversity
Beyond the lush green canopy, the rainforest is bustling with an extraordinary diversity of animal life. From colorful birds like the resplendent quetzal to elusive predators like jaguars and leopards, the rainforest offers a home to an incredible variety of species. In addition to their intrinsic value, many of these animals play vital roles in seed dispersal, pollination, and pest control, helping to maintain the rainforest’s overall health. Some fascinating examples of the animals that call these lush ecosystems home are as follows:
Mammals:
- Jaguar (Panthera onca): A powerful and elusive big cat, known for its striking coat and prowess as a top predator.
- Orangutan (Pongo spp.): Highly intelligent and gentle primates found in Southeast Asian rainforests.
- Howler Monkey (Alouatta spp.): Known for their loud vocalizations that can be heard from miles away.
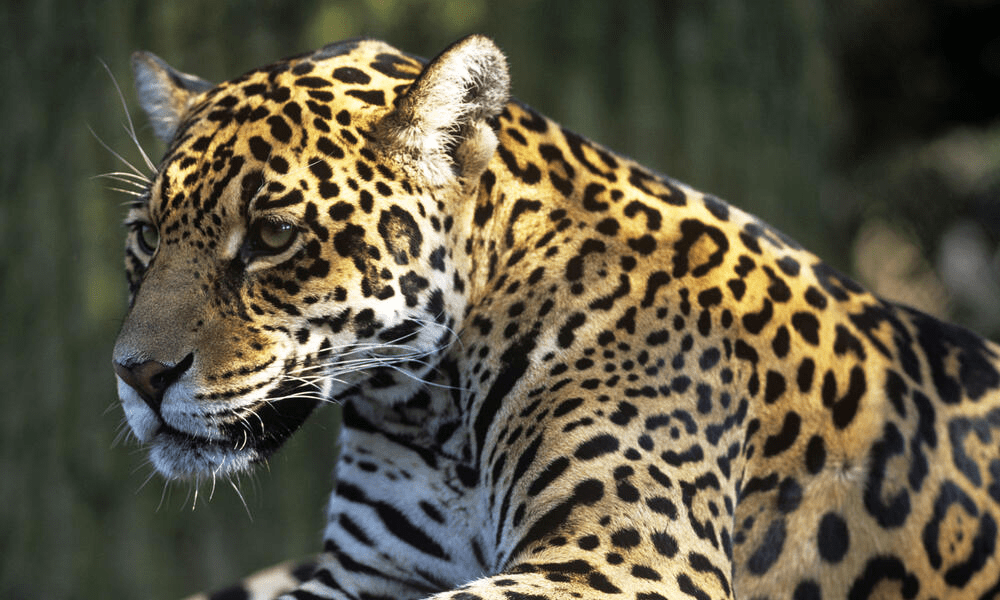
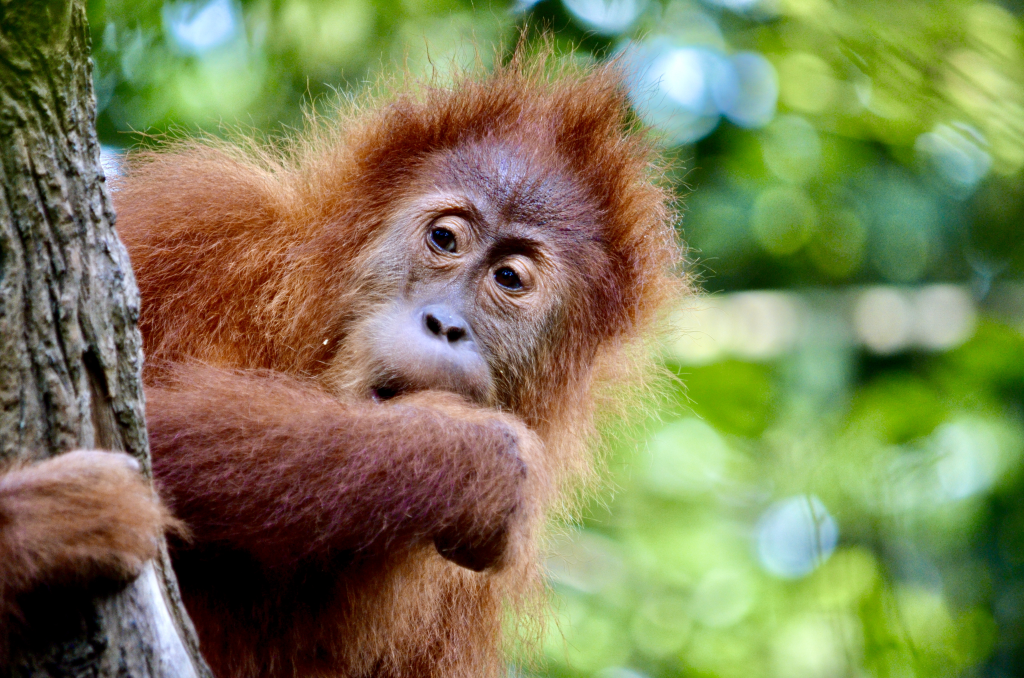


Birds:
- Harpy Eagle (Harpia harpyja): One of the largest and most powerful eagles in the world, found in Central and South American rainforests.
- Resplendent Quetzal (Pharomachrus mocinno): A brilliantly colored bird revered by ancient Mayan and Aztec civilizations.
- Toucans: Colorful birds with large, distinctive bills found in various rainforest regions.
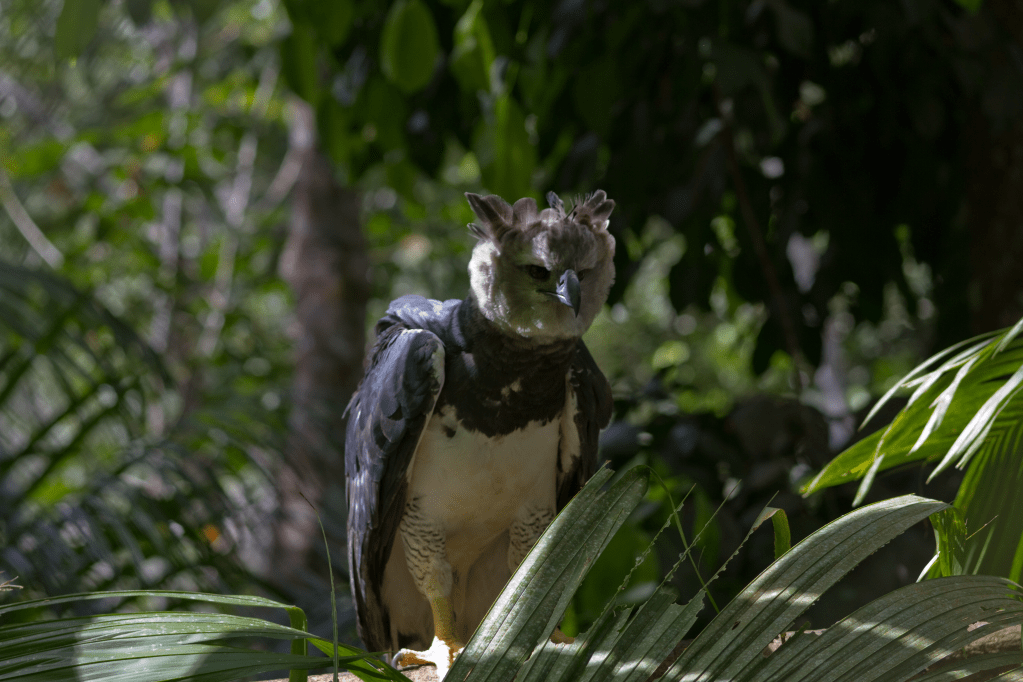
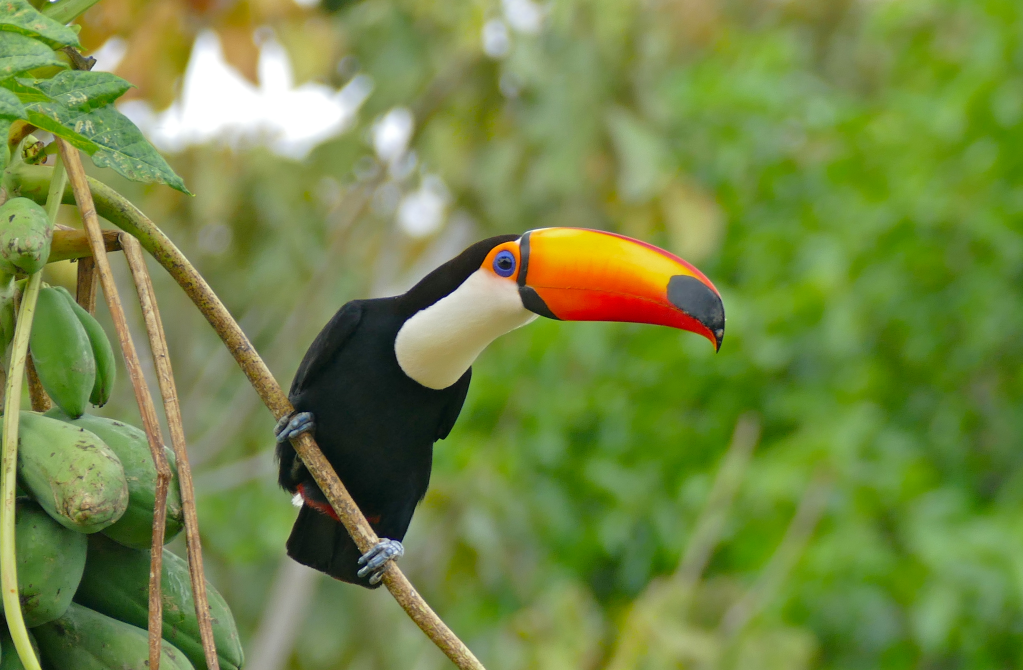


Reptiles and Amphibians:
- Poison Dart Frogs (Dendrobatidae family): Small, brightly colored frogs known for their potent skin toxins.
- Green Anaconda (Eunectes murinus): One of the largest snakes in the world, found in South American rainforests.
- Chameleon (Chamaeleonidae family): Masters of camouflage with unique eyes and long, sticky tongues.
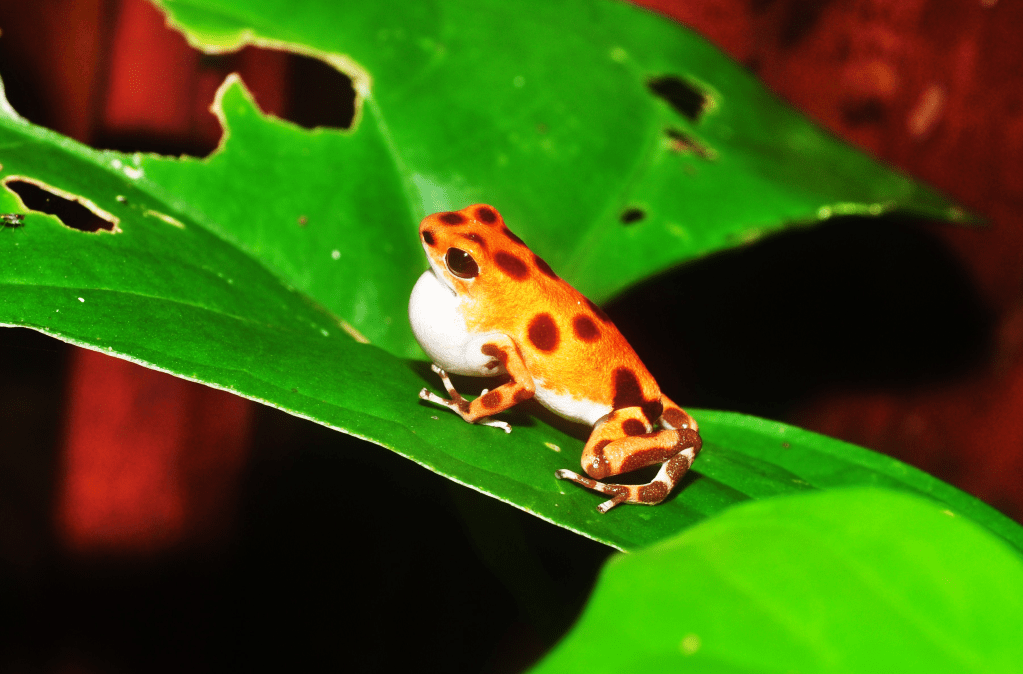
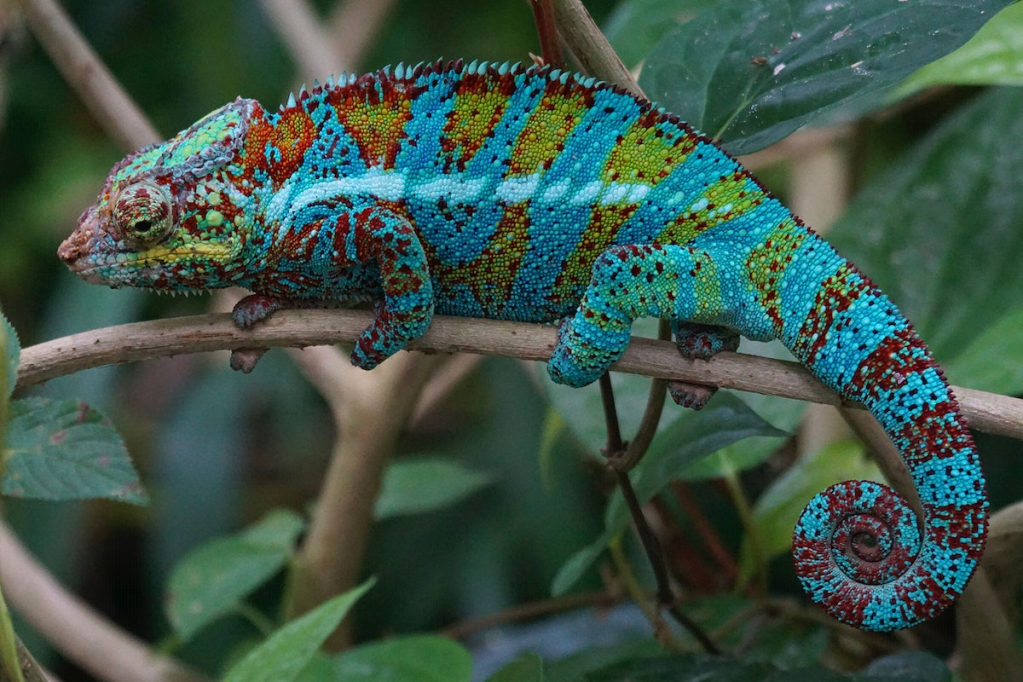


Insects:
- Atlas Moth (Attacus atlas): One of the largest moths in the world, with impressive wing spans.
- Leafcutter Ants (Atta spp.): Known for their remarkable leaf-cutting behavior and sophisticated social structures.
- Morpho Butterflies: Vibrantly colored butterflies with dazzling iridescent wings.
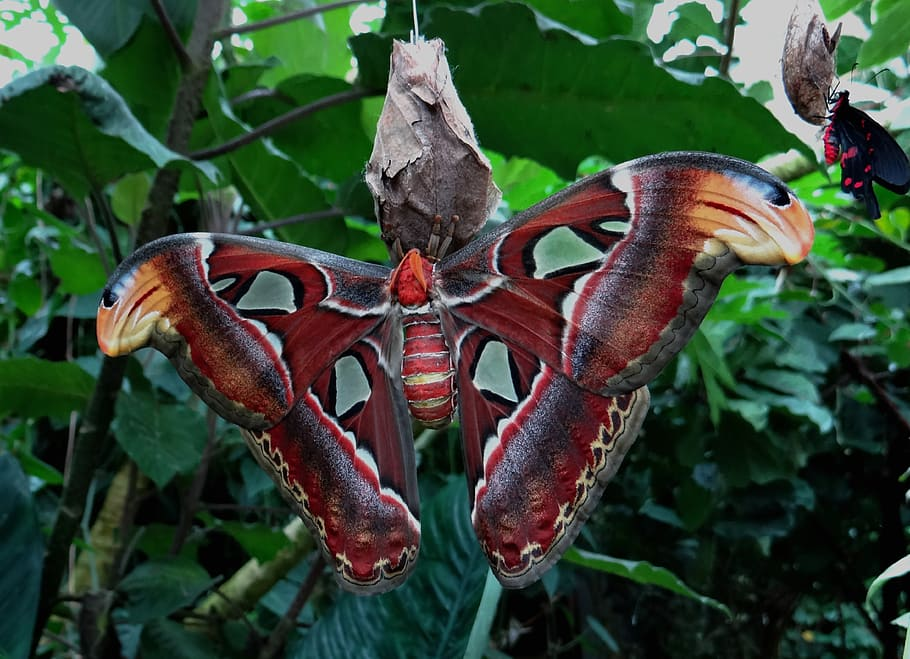
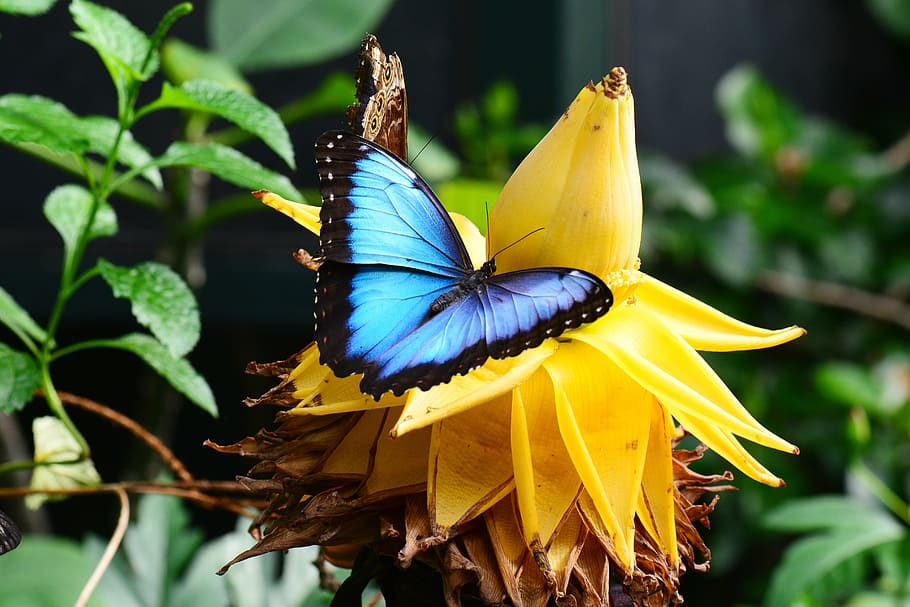


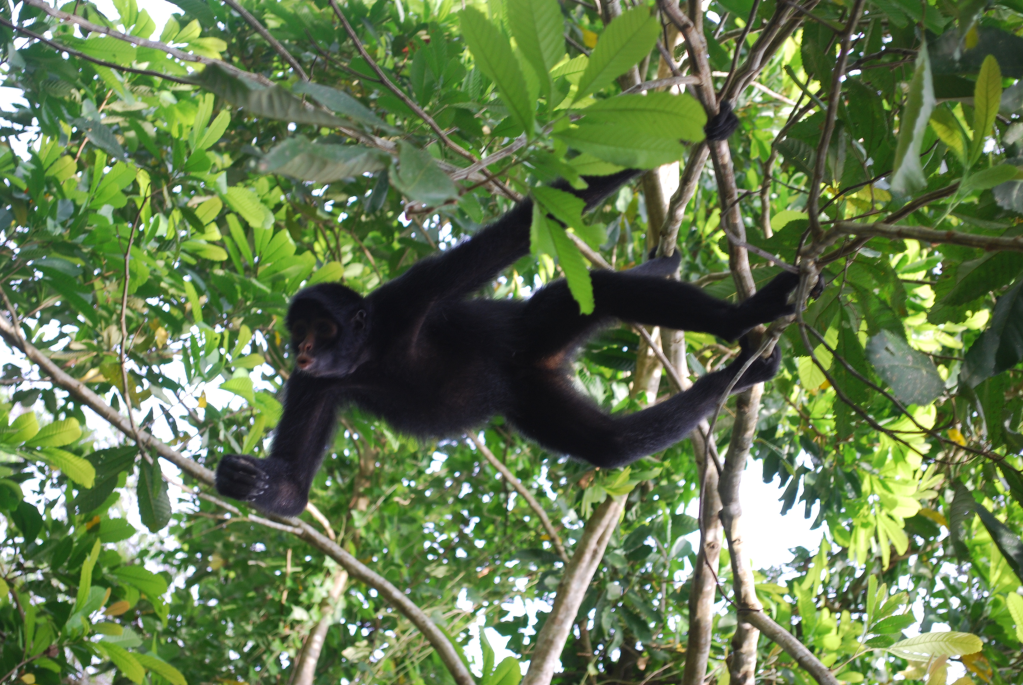
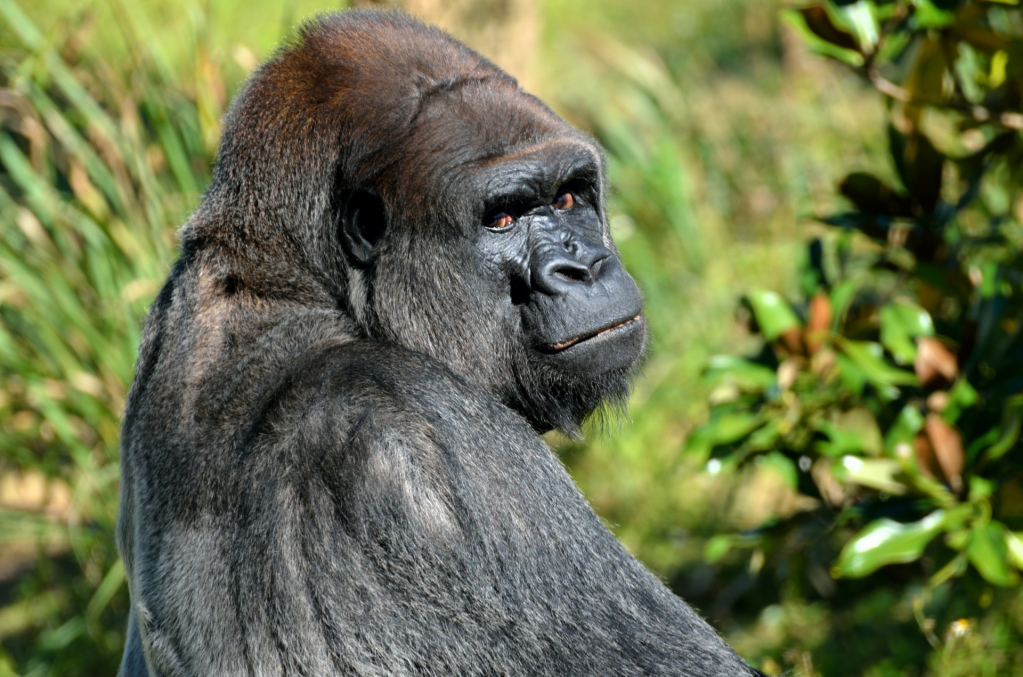
Primates:
- Spider Monkey (Ateles spp.): Agile and long-limbed monkeys adapted to life in the treetops.
- Golden Lion Tamarin (Leontopithecus rosalia): A striking and critically endangered primate native to the Brazilian rainforest.
- Western Lowland Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla gorilla): Gentle giants and one of the two species of gorillas found in African rainforests.


The Microscopic World of Insects and Microorganisms
Underneath the foliage and within the soil lie hidden worlds of insects and microorganisms. These tiny creatures may seem insignificant, but they play an indispensable role in breaking down organic matter, recycling nutrients, and supporting the entire rainforest ecosystem. From ants to bacteria, their interactions are essential for the overall health and functioning of this environment.
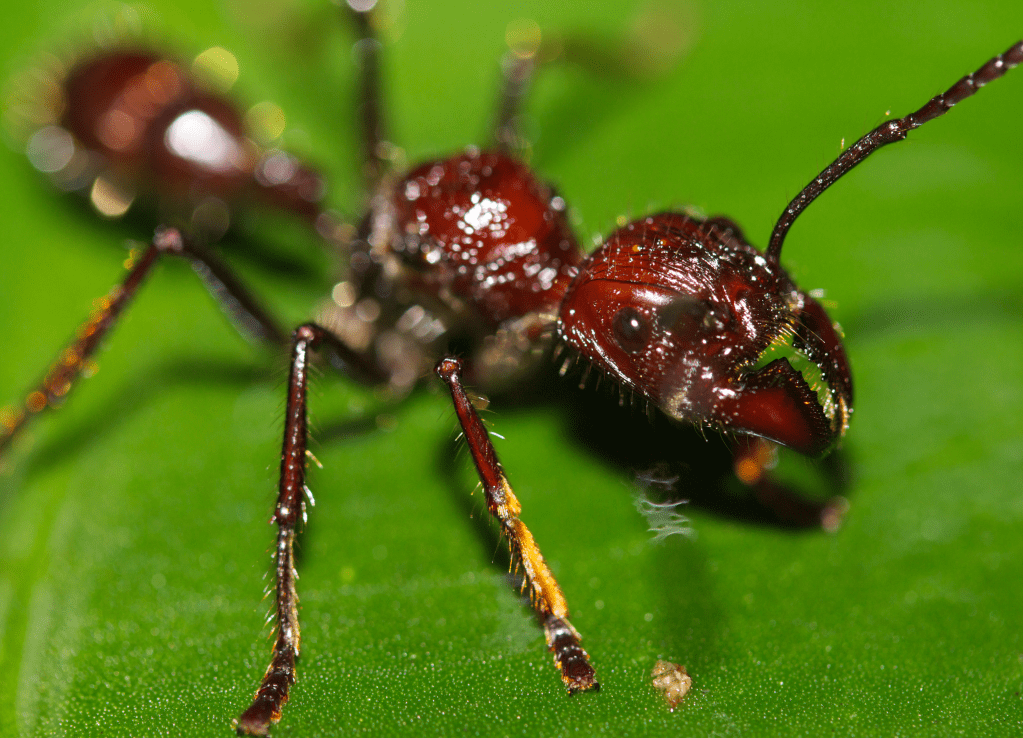
Insects:
- Bullet Ant (Paraponera clavata): Known for its intensely painful sting, it is considered to have one of the most painful insect stings in the world.
- Orchid Bees (Euglossini tribe): These bees are crucial pollinators for numerous orchid species found in the rainforest.
- Leafcutter Ants (Atta and Acromyrmex genera): These industrious ants are famous for their leaf-cutting behavior, which helps to fertilize the soil and provide substrates for cultivating fungus gardens.


Microorganisms:
- Mycorrhizal Fungi: These fungi form a symbiotic relationship with plants, helping them absorb nutrients from the soil and contributing to the overall health of the rainforest ecosystem.
- Decomposers: Various bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter, recycling nutrients, and enriching the forest floor with essential elements.
- Microscopic Protozoa: These single-celled organisms are abundant in the rainforest’s water bodies and play essential roles in nutrient cycling and aquatic food webs.
Fireflies:
- Fireflies (Lampyridae family): These bioluminescent insects create mesmerizing light displays at night, adding a magical touch to the rainforest.
Antbirds:
- Antbirds (Thamnophilidae family): Known for their specialized foraging behaviors, they often follow ant swarms to feed on insects disturbed by the ants.
Stick Insects:
- Stick Insects (Phasmatodea order): These insects are masters of camouflage, resembling twigs and branches in the rainforest vegetation.
Termite Mounds:
- Termite Mounds: These impressive structures, built by termites, are essential for nutrient cycling and serve as habitats for various other organisms.
Indigenous Peoples and Traditional Knowledge
The rich biodiversity of the rainforest has been closely intertwined with the lives of indigenous communities for centuries. These communities have accumulated extensive knowledge about the plants and animals, using them for food, medicine, shelter, and cultural practices. Preserving the rainforest means safeguarding their ancestral wisdom, which can hold the key to sustainable and harmonious living on our planet.
The Threats to Rainforest Biodiversity
Sadly, the rainforest faces significant threats from deforestation, illegal logging, mining, agriculture expansion, and climate change. As large tracts of rainforest disappear, so does the habitat of countless species, leading to alarming rates of extinction. Conserving the biodiversity of the rainforest is crucial for maintaining the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems.
The Importance of Conservation Efforts
Efforts to preserve rainforest biodiversity are more critical now than ever before. Governments, NGOs, and individuals must collaborate to establish and enforce protected areas, promote sustainable practices, and support local communities’ rights. By valuing and conserving this precious ecosystem, we can safeguard its biodiversity and ensure a healthier, more sustainable future for our planet.
Source:
- All the images are taken from the Wikipedia Commons
- https://www.greenpeace.org/usa/biodiversity-and-the-amazon-rainforest/
- https://www.internetgeography.net/topics/biodiversity-and-tropical-rainforests/
You May Also Like

