Last updated: January 2026
Golden Rice is a genetically modified rice variety designed to increase dietary vitamin A intake. It has been proposed as one of several possible interventions to address vitamin A deficiency, a public health concern in many low-income regions. Vitamin A deficiency and malnutrition often impact both human and animal ecosystems.
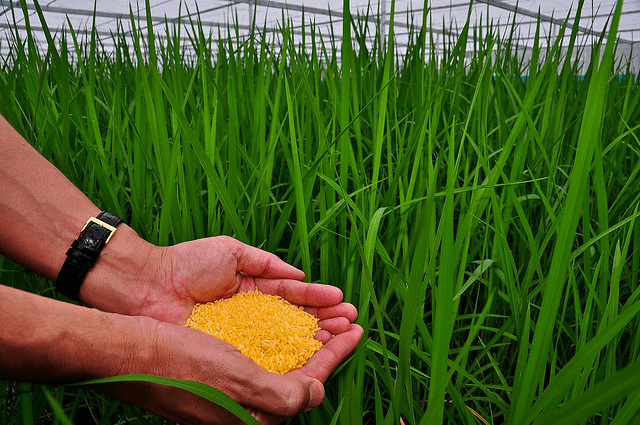
Created through genetic engineering, this rice variety contains beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, giving it a distinct golden hue. In this article, we will explore the significance of Golden Rice, its development, controversies, and its potential role in combating malnutrition and improving public health.
Why was Golden Rice Created
Vitamin A deficiency remains a major public health concern, particularly in developing countries where diets lack sufficient sources of this essential nutrient.
Similar to how nutrient cycles affect marine life, water pollution can worsen food insecurity – read about its consequences on health and ecosystems here.
This deficiency can lead to severe health consequences, including impaired vision, compromised immune function, and even blindness. Traditional dietary interventions have proven inadequate, making Golden Rice a potential game-changer in the fight against malnutrition.
Who Developed Golden Rice
Golden Rice was developed in the late 1990s by scientists Ingo Potrykus and Peter Beyer. They introduced genes responsible for beta-carotene production from daffodils and bacteria into the rice genome. The result was a rice variety rich in pro-vitamin A, offering a promising solution to combat vitamin A deficiency.
Advantages of Golden Rice:
- Improved Vitamin A Intake: Golden Rice provides a biofortified source of pro-vitamin A, addressing vitamin A deficiency and potentially reducing related health issues, such as blindness and immune system weaknesses.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Golden Rice could serve as a cost-effective intervention to combat malnutrition, as it leverages the existing rice production and distribution infrastructure.
- Potential for Enhanced Crop Yield: Since Golden Rice is genetically modified, it may have traits that improve crop resilience and yield, offering benefits to farmers and food security.
- Independence from External Supplementation: Unlike vitamin A supplementation programs that rely on external distribution and funding, Golden Rice can be cultivated locally, reducing dependency on external aid.
- Sustainable Impact: By enhancing the nutritional value of a staple crop like rice, Golden Rice could have a sustainable and long-term impact on reducing malnutrition and improving public health.
Disadvantages of Golden Rice:
- Controversy and Public Perception: The genetically modified nature of Golden Rice has sparked controversy, leading to public skepticism and reluctance to accept and adopt this crop.
- Environmental Concerns: Critics express worries about the potential ecological impact of GMOs, such as crossbreeding with wild rice varieties or the development of herbicide-resistant weeds.
- Corporate Control and Intellectual Property: The involvement of multinational corporations in Golden Rice development raises concerns about seed control and the potential exploitation of farmers.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The complex and time-consuming regulatory approval processes for GMOs in different countries can hinder the widespread adoption of Golden Rice.
- Social and Ethical Considerations: The introduction of genetically modified crops can raise ethical dilemmas regarding the unintended consequences of genetic manipulation and long-term effects on human health.
| Aspect | Golden Rice | Vitamin A Supplements | Dietary Diversification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delivery method | Staple crop | External distribution | Multiple food sources |
| Sustainability | Long-term (if adopted) | Requires ongoing funding | Depends on food access |
| Regulatory complexity | High | Low | Low |
| Public acceptance | Mixed | High | High |
| Risk concerns | GMO-related | Minimal | Minimal |
Safety, Regulation, and Scientific Consensus
Golden Rice has undergone food, feed, and environmental safety assessments in countries where regulatory approval has been granted. Regulatory authorities evaluate genetically modified crops on a case-by-case basis, considering toxicity, allergenicity, nutritional equivalence, and environmental impact.
However, approval status varies by country, and Golden Rice is not universally accepted or cultivated worldwide. Its adoption depends on national biosafety regulations, public acceptance, and alignment with broader nutrition strategies.
Potential Impact on Global Malnutrition
Proponents of Golden Rice argue that its widespread adoption could have a significant impact on global malnutrition. By providing a staple food source rich in pro-vitamin A, Golden Rice has the potential to improve the health and well-being of vulnerable populations, especially women and young children.
Golden Rice in Philippines
In a historic milestone, farmers in the Philippine Province of Antique successfully cultivated Golden Rice (Malusog Rice) on a larger scale and harvested nearly 100 tons of grains in October. This achievement marks a significant step forward in addressing vitamin A deficiency, a major health issue in the region.
The harvested grains will be distributed to households with pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, and preschool children at risk of vitamin A deficiency-related diseases. This humanitarian project represents the first practical utilization of genetic engineering to tackle a critical health problem, showcasing the potential impact of Golden Rice in improving public health. It is branded after its first variety registered in the National Seed Industry Council (NSIC) as Malusog 1 or NSIC 2022 Rc 682GR2E.
Golden Rice In India
Golden Rice is currently not approved for commercial cultivation in India. A specific event, GR2E1, has received regulatory approval for cultivation in the Philippines, where it is being grown under national biosafety regulations. Any consideration of Golden Rice for use in India would require independent, country-specific evaluations by Indian regulatory authorities, including assessments of food and feed safety, environmental impact, and biosafety. Regulatory decisions in other countries, including the Philippines, do not automatically apply to India but may inform scientific review processes in accordance with India’s agricultural and food safety frameworks.
Final Notes
Golden Rice presents an innovative approach to addressing vitamin A deficiency and combating global malnutrition. As a genetically modified crop, it offers a unique solution to a critical public health issue affecting millions.

FAQs on Golden Rice
1. What is Golden Rice?
Golden Rice is a genetically modified rice variety developed to address vitamin A deficiency, a widespread health issue affecting vulnerable populations in developing countries.
2. How is Golden Rice different from regular rice?
Golden Rice is genetically engineered to contain beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, which gives it a distinctive golden hue. Regular rice lacks this naturally occurring nutrient.
3. Why is Golden Rice important?
Golden Rice has the potential to combat vitamin A deficiency, which can lead to severe health consequences, including blindness, weakened immune systems, and delayed growth and development.
4. Is Golden Rice safe to eat?
Golden Rice approved for cultivation has undergone food and environmental safety assessments by national regulatory authorities. Safety conclusions depend on country-specific evaluations, and approval does not automatically apply globally.
5. Is Golden Rice approved for commercial use? Golden Rice has received regulatory clearance for cultivation in the Philippines. However, its commercial use in other countries is subject to individual regulatory approvals.
6. Can Golden Rice be a sustainable solution for malnutrition?
The potential sustainability of Golden Rice depends on various factors, including regulatory acceptance, public perception, and equitable distribution to vulnerable populations. Long-term success will require collaborative efforts from multiple stakeholders.
Source:
- https://www.science.org/content/article/bangladesh-could-be-first-cultivate-golden-rice-genetically-altered-fight-blindness
- https://www.philrice.gov.ph/malusog-rice-harvested/
- https://www.newindianexpress.com/states/telangana/2022/dec/20/golden-rice-provides-simple-solution-to-vitamin-deficiencyiirr-director-2529889.html