Last updated: 2026
Biodiversity hotspots are regions of the world that are exceptionally rich in plant and animal species but are also under severe threat from human activities. These areas play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, supporting ecosystem services, and sustaining life on Earth.
Despite covering only a small fraction of the planet’s land surface, biodiversity hotspots support a disproportionately high number of endemic species. Protecting these regions is essential for conserving global biodiversity and ensuring long-term environmental stability.
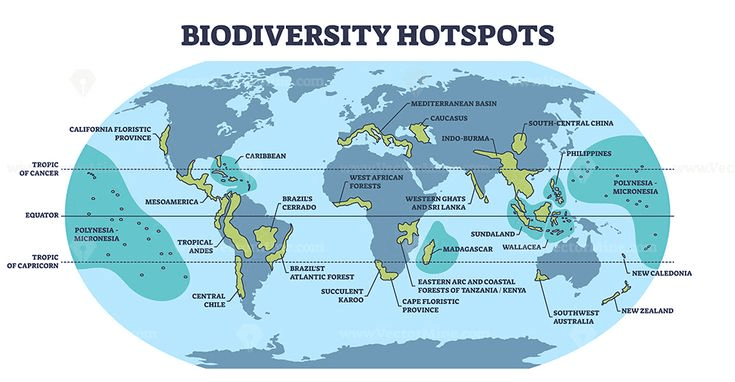
What Is a Biodiversity Hotspot?
A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region that meets two strict criteria:
- It contains at least 1,500 endemic plant species (found nowhere else on Earth)
- It has lost at least 70% of its original natural habitat
These criteria were established by conservation biologist Norman Myers to prioritize areas that are both biologically rich and highly threatened.
👉 To understand why species diversity matters, read: Importance of Biodiversity
🌍 Biodiversity Hotspots at a Glance
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Total hotspots worldwide | 36 |
| Land area covered | ~2.3% of Earth’s surface |
| Plant species supported | >50% of global endemics |
| Vertebrate species | ~43% |
| Main threats | Deforestation, climate change, pollution |
📌 Why this matters: Protecting hotspots yields maximum conservation impact with limited resources.
Why Are Biodiversity Hotspots Important?
Biodiversity hotspots are critical because they:
- Support unique and endemic species
- Regulate climate and water cycles
- Provide food, medicine, and livelihoods
- Act as buffers against natural disasters
- Maintain ecosystem resilience
The loss of hotspots accelerates species extinction and disrupts ecological networks.
👉 Related concept: Keystone Species and Ecosystem Stability
Major Biodiversity Hotspots of the World
1️⃣ Tropical Rainforests
Examples: Amazon Basin, Congo Basin
- Extremely high species richness
- Major carbon sinks
- Severe threat from deforestation
👉 Related reading: The Incredible Biodiversity of the Rainforest

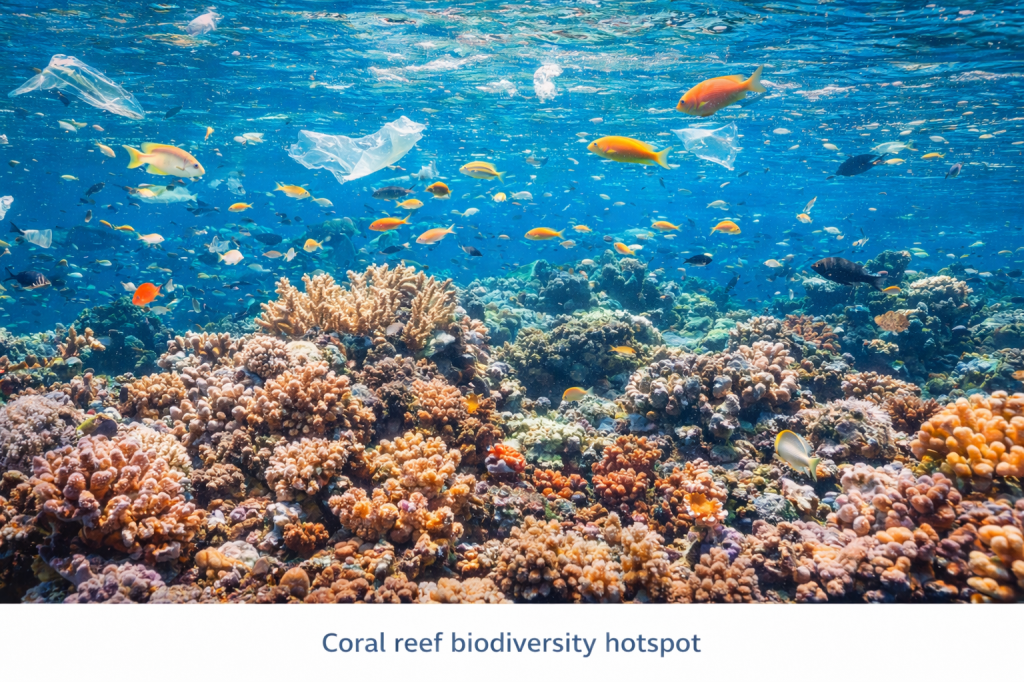
2️⃣ Coral Reef Systems
Examples: Coral Triangle, Great Barrier Reef
- Support ~25% of marine species
- Highly sensitive to temperature rise
- Threatened by ocean acidification and pollution

3️⃣ Mediterranean-Type Ecosystems
Examples: Mediterranean Basin, California Floristic Province
- High plant endemism
- Vulnerable to urbanization and wildfires
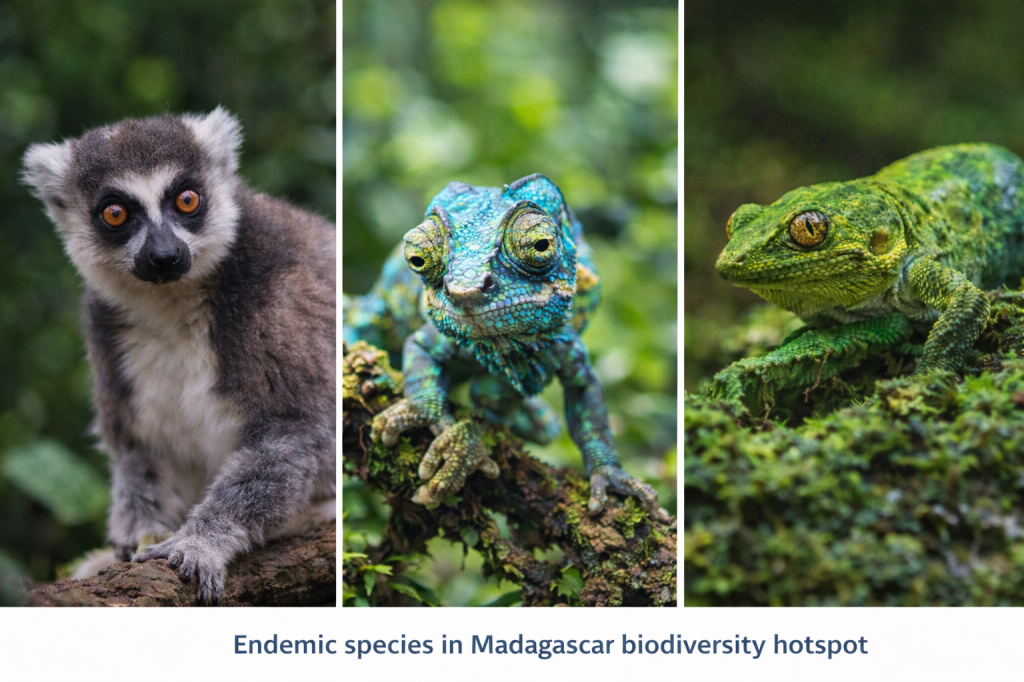
4️⃣ Island Biodiversity Hotspots
Examples: Madagascar, Philippines
- High endemism due to isolation
- Extremely vulnerable to habitat loss and invasive species
👉 Explore: Madagascan Faunal Subregion

Key Threats to Biodiversity Hotspots
| Threat | Impact |
|---|---|
| Habitat fragmentation | Species isolation & extinction |
| Climate change | Range shifts & coral bleaching |
| Water pollution | Ecosystem collapse |
| Overexploitation | Population decline |
| Invasive species | Native species displacement |
Conservation Strategies for Biodiversity Hotspots
Effective conservation requires a multi-layered approach:
- Establishing protected areas
- Promoting sustainable land use
- Supporting indigenous stewardship
- Enforcing environmental regulations
- Restoring degraded habitats
Long-term success depends on integrating conservation with local economic development.
Biodiversity Hotspots and Climate Change
Climate change intensifies existing threats by:
- Altering temperature and rainfall patterns
- Increasing extreme events (fires, floods)
- Disrupting species interactions
Hotspots with narrow climatic tolerance are especially vulnerable.
👉 Related: Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity
Final Thoughts
Biodiversity hotspots represent the irreplaceable core of life on Earth. Although they occupy a small portion of the planet, their loss would have catastrophic ecological and social consequences.
Protecting these regions is not optional—it is essential for sustaining biodiversity, human well-being, and planetary health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
❓ What is a biodiversity hotspot?
A biodiversity hotspot is a region rich in endemic species that has lost most of its natural habitat and is under severe threat.
❓ How many biodiversity hotspots exist worldwide?
There are currently 36 recognized biodiversity hotspots.
❓ Why are biodiversity hotspots under threat?
Major threats include deforestation, climate change, pollution, habitat fragmentation, and overexploitation of resources.
❓ Are biodiversity hotspots only found on land?
Most hotspots are terrestrial, but some include coastal and marine ecosystems, such as coral reefs.
❓ How can biodiversity hotspots be protected?
Through protected areas, sustainable development, habitat restoration, and community-led conservation efforts.

