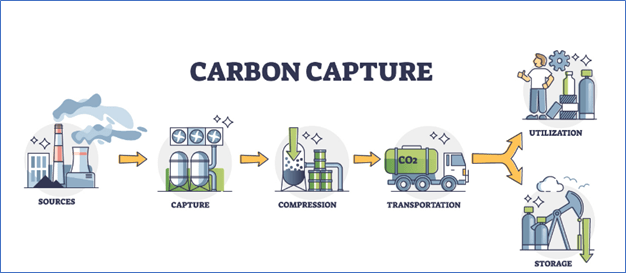
The world is facing climate change. It is of utmost importance to control the rising temperature of the atmosphere of the planet. Carbon dioxide is known to be the most effective greenhouse gas contributing to climate change. Hence, scientists and researchers have designed a system called carbon capture. Carbon capture is a process that captures carbon dioxide in the atmosphere or from water and can be stored or utilized for any other purpose. This process is done by mechanical processes with the use of machines. The removal of CO2 from the atmosphere or water can contribute to reducing the rising temperature of the globe.
To capture the carbon naturally, there are carbon sinks present in nature in the form of forests, oceans, and soil. But the amount of carbon dioxide we are producing is exceeding the threshold of the carbon dioxide captured by these carbon sinks. Hence, we need to develop artificial carbon capture sinks that can remove the excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. After capturing the carbon, it can be stored underground or can be utilized for different applications like building materials, biofuels, and biomass.
Race to carbon capture and removal from the atmosphere or water is the mission of the X Prize where the prize of 100 Million USD will be awarded to the team of inventors that invent or design the technology to capture/remove carbon from the atmosphere or water. This competition is Funded by Elon Musk and the Musk Foundation, this $100M competition is the largest incentive prize in history, an extraordinary milestone. The competition is on and will be concluded in the year 2025. To know more about this competition and to follow for updates, the readers can check out the official website for the same.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) is a term used for a set of technologies that help to mitigate carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from major point of sources such as power plants, refineries, and other industrial facilities thus removing excess CO2 from the atmosphere. This technology has the potential and is expected to work towards achieving global climate targets. Global organizations such as the International Energy Agency (IEA), International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) have all produced long-term energy outlooks that rely on a rapid expansion of CCUS in order to limit global temperature rise to 1.5°C.
The CCUS system has the potential to play a key role in the efforts towards global decarbonization in several ways, such as: 1. Decreasing CO2 emissions in ‘hard-to-abate’ industries, where it is especially difficult to decarbonize the processes. 2. Production of low-carbon electricity and hydrogen, that may be applied to decarbonize different activities and 3. Decreasing the quantity of existing CO2 from the atmosphere. The different applications of CCUS can produce clean energy in diverse and flexible manner, thus in turn providing energy security, that has recently become a major priority for countries around the world.
CCUS is known to be the most cost-effective technology in different regions for the deep decarbonization of several hard-to-abate businesses, like iron, steel, and chemicals. Further, CCUS is practically the only known technology to achieve deep emissions cuts in cement manufacture, an industry that produces almost 7% of the world’s emissions.
As a way of producing electricity and hydrogen in a low-carbon manner, CCUS can become the next big alternative to replace fossil fuels. The CCUS technology can be easily installed on power plants running on different energy resources like coal, gas and waste. The low-carbon electricity produced will be an alternative to fossil fuels for energy resources, that include personal transport, heating and warming-like extraction of low- and medium-temperature heat in industry. On the other hand, hydrogen will be used as a substitute for fossil fuels in combustion processes, as feedstock in industrial applications, or in long-run transportation.
Increasing evidence shows that carbon dioxide removal from the atmosphere can be instrumental to attaining net zero emissions worldwide. The latest IPCC assessment report states that the deployment of carbon dioxide removal (CDR) technologies is necessary to achieve net zero emissions. Two of the main ways of removing CO2 from the atmosphere – bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) and direct air carbon capture and storage (DACCS) – both share a technological foundation with CCUS. DACCS enables the capture of CO2 directly from the atmosphere while BECCS can result in CO2 removal on a net basis where the biomass is sustainably sourced.
Algae is the next generation of Carbon capture. Algae is a microscopic organism that can perform photosynthesis just like trees and plants. Hence, algae are able to capture CO2 in the presence of sunlight during photosynthesis and utilize carbon dioxide in the synthesis of sugars. Photosynthesis is the mature way to capture and utilize carbon dioxide to maintain its levels in the atmosphere. A company called Brilliant Planet has researched for over a decade on studying algae and developing its proprietary production process. Brilliant Planet co-founder Raffael Jovine quoted ”Algae are inherently more efficient carbon-removal machines than terrestrial plants as they don’t spend biological resources on building a supporting infrastructure of trunks, roots, and branches — their entire surface area is dedicated to photosynthesis.” Algae not only is used to capture carbon and fix it in the form of sugars using photosynthesis but in the same photosynthetic process, oxygen is produced which is cooling the temperature of the atmosphere. Another major advantage of algae for carbon capture is that there are many applications of algal biomass that have value added to the entire capture process. For example, when algae is cultivated and utilized for carbon capture, the algal biomass produced can be useful as a biofuel, protein extraction, and nutrition extraction, etc.
Carbon capture is quite technical in nature, but that does not mean that the common man should not know anything about it. As sustainability takes a major factor in our day-to-day lives, it is our responsibility to understand the recent developments in our fight against climate change.
Reference: