Water and sunlight have allowed life to thrive on our planet. We can find beautiful plants, flowers, and animals wherever we go. These two things are essential for any ecosystem. The terms “flora” and “fauna” show the wide variety of life on our planet.
There are two main types of life on Earth: plants (flora) and animals (fauna). But the planet also supports other forms of life that are harder to see. In this article, we’ll learn about flora and fauna. We’ll understand their importance in the ecosystem and their role.
What is Flora?
“Flora” is the name for all the plants that grow or have grown in a certain area or time. The term “flora” usually refers to the native plants that naturally grow in a place. But it can also include new plant species that have been brought to the area.

The term “flora” comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants and flowers. In Roman mythology, Flora represented the goddess of flowers and spring. Flora was a symbol of nature, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology.
Plants can be identified from one another in a variety of ways on the planet. The easiest way is to divide by location. Plants in the mountains are very different from plants in the desert.
Plants found underwater are a unique type of flora. Scientists also study ‘Fossil Flora,’ which are prehistoric plants. The world’s current plants and animals are classified based on their natural environment.
‘Native Flora‘ refers to plants that are native to a specific area. Cacti are a type of desert plant found all over the world. They can grow in different climates, but they are native to desert sand dunes.
‘Agricultural Flora,’ refers to plant life that has been cultivated by people for a specific purpose. Plants planted for decorative purposes are referred to as ‘Garden Flora’ or ‘Horticultural Flora.’ Then there’s the ‘Weed Flora,’ which consists of plants that are either unwanted in particular locations or invasive in native plant life.
Flora comprises a vast variety of plant life. Each species is uniquely adapted to its habitat and ecological niche. Some key categories of flora include:
- Trees: Provide habitat and mitigate climate change.
- Shrubs: Offer shelter and nutrition to animals and insects.
- Grasses: Dominate grasslands and play a crucial role in soil stabilization.
- Herbs: Contribute to biodiversity and pollinator interactions.
- Aquatic Plants: Essential components of freshwater and marine ecosystems.
Roles of Flora
Flora plays many vital roles in ecosystems, contributing to the overall health and functioning of the planet:
- Photosynthesis and Oxygen Production: Plants convert carbon dioxide and sunlight into energy, releasing oxygen as a byproduct—a foundation of life on Earth.
- Carbon Sequestration: Plants capture and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, reducing greenhouse gas concentrations and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
- Habitat and Food: Flora provides habitats for a wide range of animal species, offering shelter, nesting sites, and food sources.
- Soil Stabilization: Plant roots prevent erosion and maintain soil structure, crucial for nutrient cycling and water retention.
- Pollination: Many plants rely on animals for pollination, ensuring reproduction and genetic diversity.
- Medicinal and Cultural Uses: Flora has provided medicinal compounds, food, shelter, and cultural significance for diverse communities throughout history.
Examples of Flora
Sunflower (Helianthus annuus):
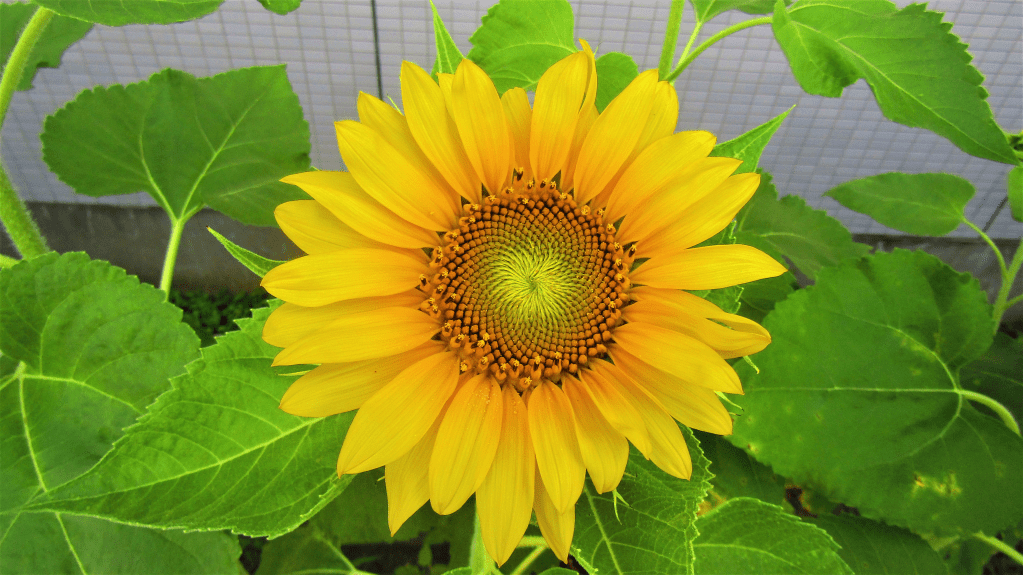

Sunflowers are tall, yellow flowers that track the sun. They are famous for their edible seeds and sunflower oil production, and are commonly cultivated for their delightful appearance.
Maple Tree (Acer saccharum):

Maple trees are known for their beautiful, hand-shaped leaves that change color in the fall. They also produce sweet sap, which is used to make maple syrup, a delicious topping for pancakes and waffles.
Cactus (Cactaceae family):
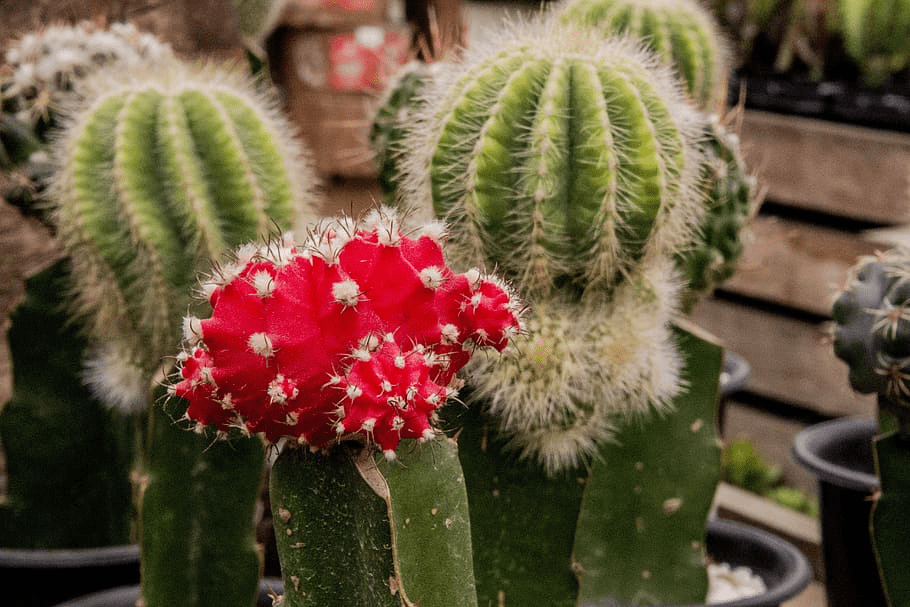

Cacti are plants suited to hot, dry environments. They have thick, water-storing stems and spines instead of leaves, which help protect them from animals and reduce water loss. Cacti come in various shapes and sizes and are well-adapted to desert life.
Venus Flytrap (Dionaea muscipula):

The Venus Flytrap is a carnivorous plant found in the southeastern United States. It has unique leaves with sensitive hairs that, when touched by an insect, cause the leaves to close and trap the insect for digestion to obtain nutrients.
Redwood Tree (Sequoia sempervirens):
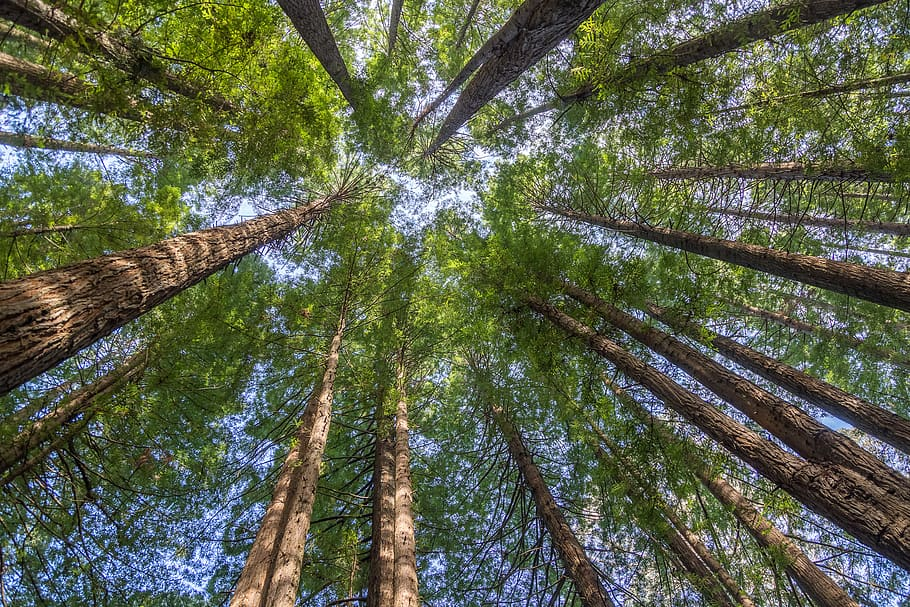

Redwood trees can grow over 300 feet tall with reddish-brown bark, living for thousands of years. They are mainly found in California and are some of the tallest living organisms on Earth.
Check out this video from National Geographic to know the amazing wild flora that will amaze you.
What is Fauna?
Fauna includes animals that live or have lived in a specific place or time. The term comes from the ancient Roman religion, where Fauna is believed to be the goddess who nurtures all that is useful to living creatures.
The earth has various divisions of flora and fauna. Animal life is more diverse, making the divides more complex than those of plants.
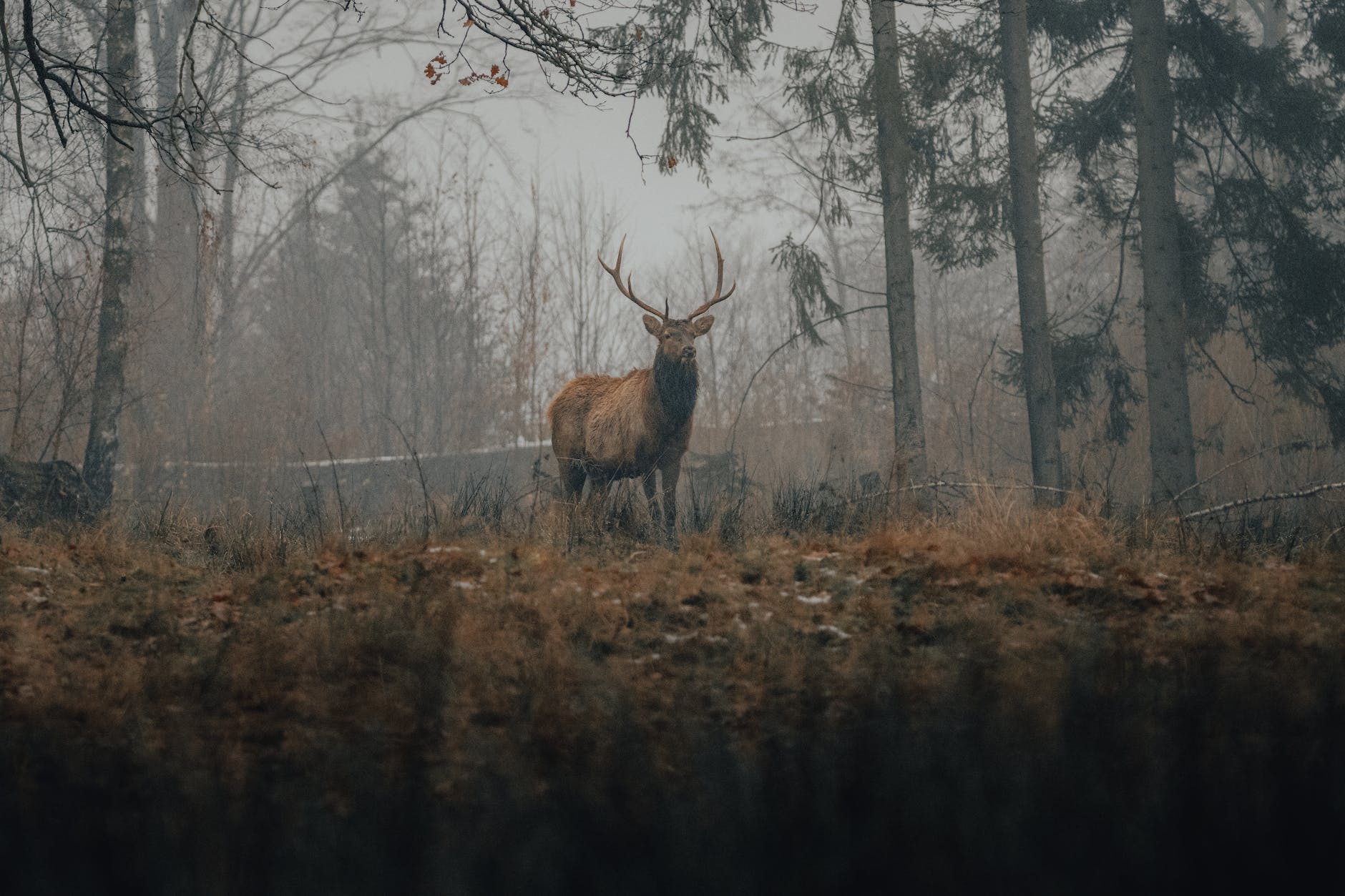

To start, “Fauna” refers to all animal species. Within it, we have “Avifauna” for birds, and “Piscifauna” for fish. These classifications exclude bacteria and viruses, which are tiny single-celled creatures.
They also ignore the tiny organisms that are plentiful in nature but cannot be seen with the naked eye. ‘Microfauna‘ refers to this type of animal life. While much of the earth’s plant and animal life is visible, a significant amount remains unnamed or undiscovered.
This is the reason we have categories like ‘Cryptofauna’ for exceptionally rare and possibly mythical species, ‘Microfauna’ for incredibly small animals, and ‘Megafauna’ for the larger animals we commonly encounter.
Fauna encompasses a wide range of animal life, with each species shaped by evolution to thrive in specific habitats and niches. Whether in the air, on land, or in the ocean depths, fauna demonstrates impressive adaptation and diversity, highlighting key categories such as:
- Mammals: Warm-blooded animals with hair or fur and mammary glands, exhibiting diverse reproductive and survival strategies.
- Birds: Feathered creatures with beaks, known for their remarkable ability to fly and inhabiting various habitats.
- Reptiles: Include snakes, lizards, turtles, and crocodiles, exhibiting a wide range of survival adaptations.
- Amphibians: Such as frogs, toads, and salamanders, with both aquatic and terrestrial life stages, serving as environmental health indicators.
- Fish: Adapted to aquatic environments, with diverse forms, from sharks to tropical reef fish.
- Insects and Invertebrates: Insects, including bees, butterflies, ants, and beetles. Invertebrates lack a backbone and include creatures like spiders, snails, and jellyfish.
Roles of Fauna in Ecosystems
- Predation and Herbivory: Fauna participate in complex food chains and webs, with predators maintaining prey populations and herbivores controlling plant growth.
- Pollination: Many fauna species, such as bees, butterflies, and bats, play a vital role in pollination, facilitating plant reproduction and the production of fruits and seeds.
- Scavenging and Decomposition: Scavengers, like vultures and hyenas, contribute to ecosystem health by consuming dead remains and aiding in nutrient cycling.
- Seed Dispersal: Fauna, from birds to mammals, assist in seed dispersal by ingesting seeds and transporting them to new locations, contributing to plant colonization.
- Bioturbation: Burrowing animals, like earthworms and burrowing owls, alter soil structure and nutrient availability through their activities.
- Ecosystem Engineers: Certain fauna species, like beavers, alter their habitats by building dams and lodges, influencing water flow and creating new environments.
Examples of Fauna
Penguin (Spheniscidae family):
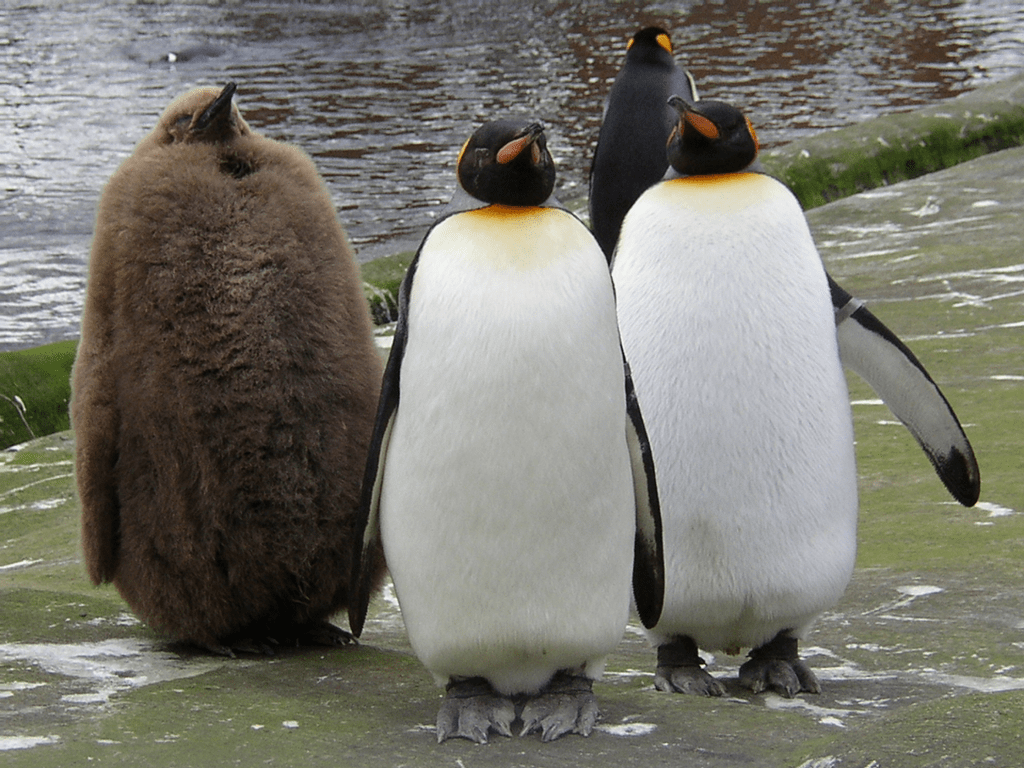

Penguins are birds that cannot fly, and are mainly found in the Southern Hemisphere, especially in Antarctica. They are strong swimmers and use their wings as flippers. When on land, penguins often move in a distinctive waddling manner and have a black and white coloration.
Koala (Phascolarctos cinereus):
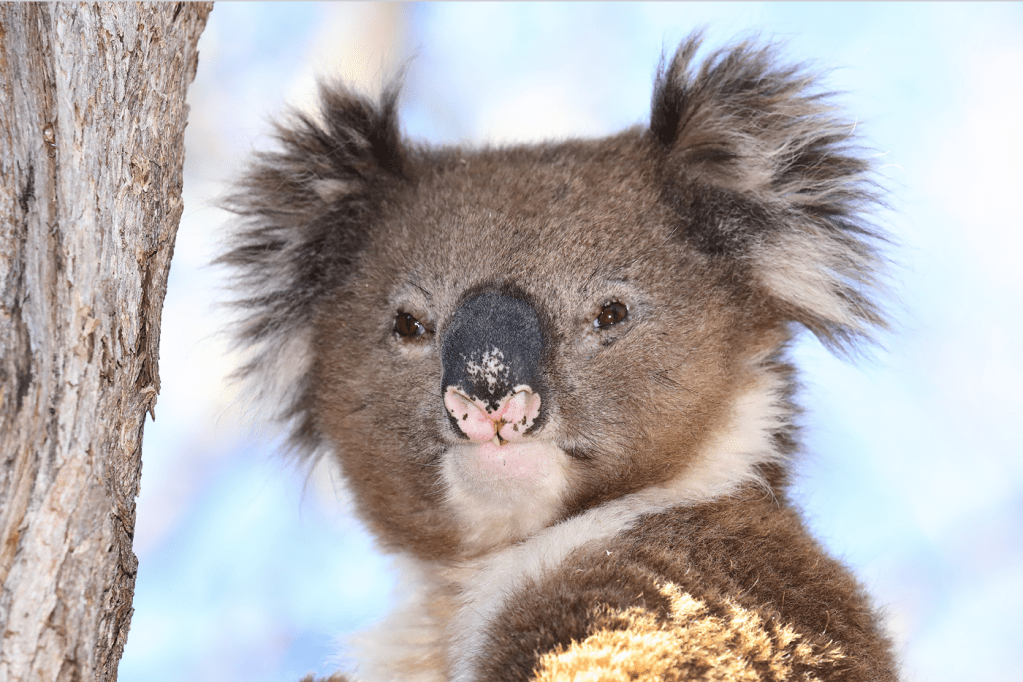

Koalas are native to Australia and known for their fluffy gray fur, round faces, and diet of eucalyptus leaves. They spend most of their time in trees.
Butterfly (Lepidoptera order):

Butterflies are insects with colorful, delicate wings. They undergo metamorphosis, starting as caterpillars and transforming into butterflies. They play a vital role in pollinating flowers and are admired for their beauty.
Lion (Panthera leo):
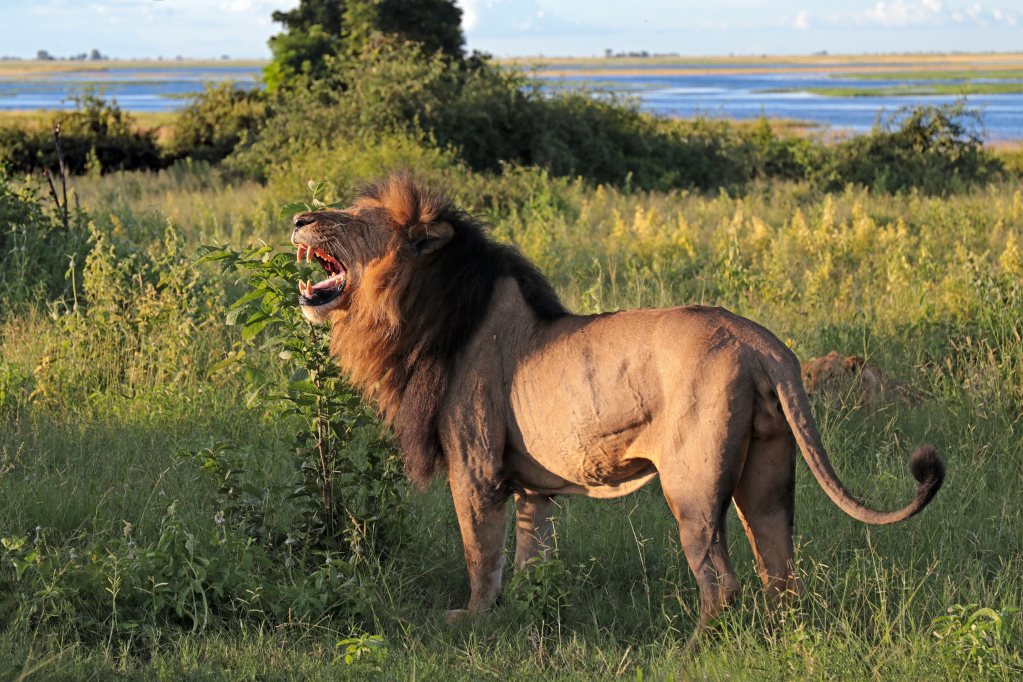

Lions are large, majestic cats found in Africa. They are known for their social behavior, living in groups called prides. Male lions often have impressive manes, while females do most of the hunting for the pride.
Dolphin (Delphinidae family):
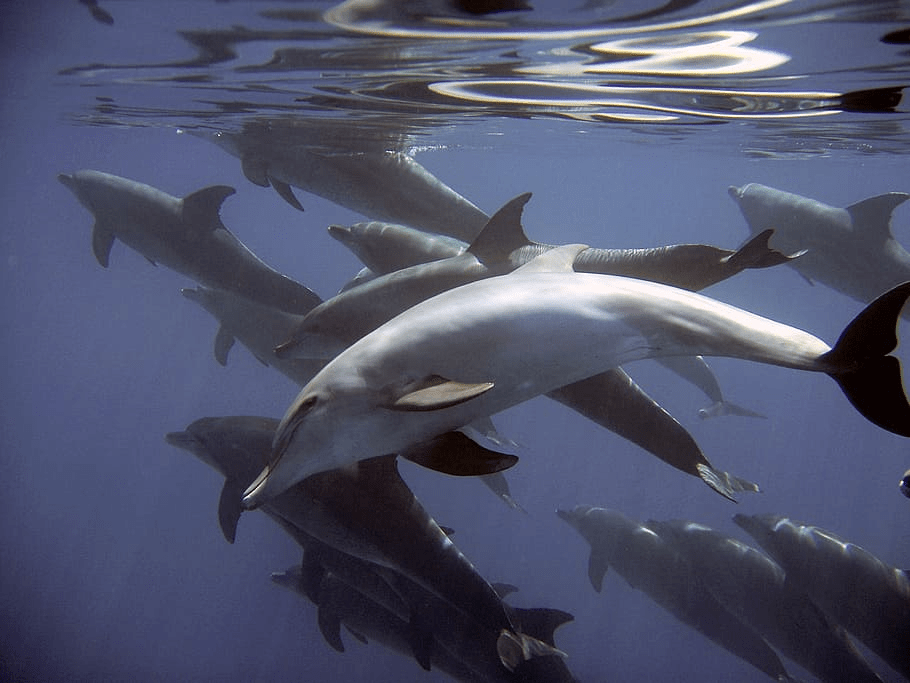
Dolphins are intelligent marine mammals known for their playful behavior and distinctive dorsal fins. They are excellent swimmers and often leap out of the water. Dolphins communicate using clicks and whistles and are found in oceans worldwide.
Also Read: 15 Fascinating Facts About Dolphins
Check our this amazing video from National Geographic on the amazing wildlife from Nile
Importance of Flora and Fauna
Plants, like trees and flowers, are important because they give us oxygen and absorb carbon dioxide, which is good for the environment. They also give us food, medicine, and materials like wood and cotton.
We get some medicines from plants and animals, like aspirin from willow trees and certain cancer treatments from plants. Animals, such as leeches and bees, also help in making medicines. Protecting plants and animals ensures we have new sources for medicine.
Animals, like birds and insects, help in different ways, like spreading seeds and keeping the soil healthy. They also control pests and help in recycling nutrients.
Plants and animals also help local businesses. Many communities depend on plants and animals for their jobs. Industries like farming, fishing, and tourism rely on healthy plants and animals. When we protect them, we also support these businesses.
Both plants and animals help create biodiversity, which makes environments stronger and more productive. Biodiversity makes sure all living things can survive in a natural way.
Conservation of Flora and Fauna
People need animals and plants for resources, so it’s important to protect where they live. In Africa, forests are often turned into farmland, causing a loss of different kinds of plants and animals. Around the world, coastal mangroves are being replaced by farming and fish farming, while cities destroy where many species live. That’s why we need to protect these places.
As people in developing countries have more money, they can buy more meat. This means we need more meat, which uses up our natural resources. For example, the grains used to feed cows in the United States could feed 800 million people. So, making the choice to eat less meat can help reduce the demand for resources like food, water, and space.
Market forces are making animals and plants harder to find. Elephants and rhinos in Africa are hunted by poachers, so there are fewer of them. This makes the ivory and horns from these animals more valuable. The prices of Asian woods like rosewood have also gone up. To protect these resources, we need to go against the market, like making laws to ban ivory and limit the export of wood.
To help with conservation, we make safe areas like national parks and wildlife reserves. These areas give plants and animals a safe place to live. Laws and rules also help protect animals that are in danger of being hunted or losing their homes.
We can all help with conservation. Easy things like planting trees, making less trash, and using fewer chemicals can make a big difference. Also, it’s important to support conservation groups and tell people about the issues facing plants and animals.
Final Words
Flora and fauna are essential for Earth’s ecosystems, playing vital roles in nutrient cycling, pollination, food chains, and ecosystem balance. It’s a reminder of the need to maintain balance to preserve their diversity and the services they provide.
References
- Testbook: Understanding Flora and Fauna
- Infinity Learn: Flora and Fauna
- Gondwana University: Difference Between Flora And Fauna
MCQs on Flora and Fauna
- What does the term “flora” refer to?
- a) Animal life
- b) Plant life
- c) Aquatic life
- d) Microbial life
- What does the term “fauna” refer to?
- a) Plant life
- b) Animal life
- c) Aquatic life
- d) Microbial life
- Which of the following is a key role of both flora and fauna in ecosystems?
- a) Carbon sequestration
- b) Volcanic activity
- c) Atmospheric erosion
- d) Solar radiation
- What is the primary role of flora in nutrient cycling?
- a) Oxygen production
- b) Carbon sequestration
- c) Soil stabilization
- d) Photosynthesis
- What role do scavengers play in ecosystems?
- a) Pollination
- b) Seed dispersal
- c) Decomposition
- d) Predation
- What is the primary function of the ozone layer in the stratosphere?
- a) Absorbing visible light
- b) Emitting ultraviolet radiation
- c) Filtering harmful ultraviolet radiation
- d) Producing oxygen molecules
- Which group of animals is known for its ability to fly?
- a) Mammals
- b) Reptiles
- c) Amphibians
- d) Birds
- How do many plants rely on fauna for reproduction?
- a) Through photosynthesis
- b) Through seed dispersal
- c) Through carbon sequestration
- d) Through soil stabilization
- What is an essential role of pollinators like bees and butterflies?
- a) Seed dispersal
- b) Decomposition
- c) Nutrient cycling
- d) Plant reproduction
- How does habitat loss impact both flora and fauna?
- a) Enhances species diversity
- b) Provides new habitats
- c) Threatens survival
- d) Promotes migration
- What is a common challenge faced by both flora and fauna due to climate change?
- a) Increased habitat availability
- b) Decreased competition
- c) Disruption of behavior and breeding
- d) Improved reproductive success
- Which term encompasses both plant and animal life?
- a) Flora
- b) Fauna
- c) Biodiversity
- d) Ecosystem
- Why is the conservation of both flora and fauna important?
- a) For aesthetic purposes only
- b) To maintain ecosystem balance
- c) To prevent pollution
- d) To increase urbanization
Answers:
- b) Plant life
- b) Animal life
- a) Carbon sequestration
- d) Photosynthesis
- c) Decomposition
- c) Filtering harmful ultraviolet radiation
- d) Birds
- b) Through seed dispersal
- d) Plant reproduction
- c) Threatens survival
- c) Disruption of behavior and breeding
- c) Biodiversity
- b) To maintain ecosystem balance
Note: All images from taken from the Wikipedia Commons
Subscribe
Subscribe to my newsletter
Follow us on twitter @DecodingBiosph1
You May Also Like


One thought on “What is Flora and Fauna: Importance, Examples and MCQs”